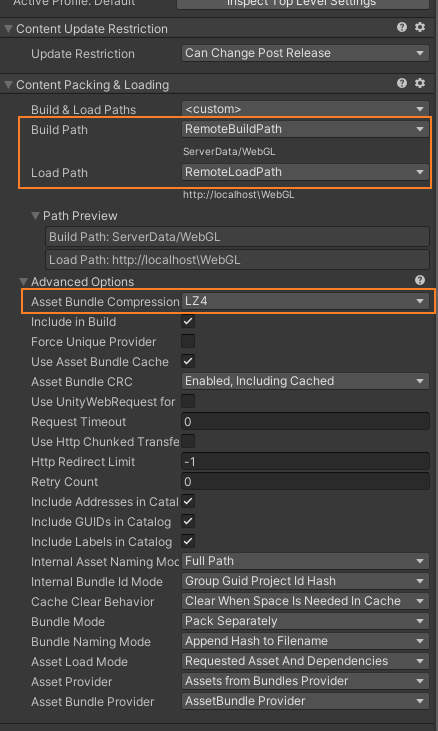
首先 yml文件中的自定义配置如下
login-type-config:
types:
k1: "yuheng0"
k2: "yuheng1"
我们有两个对应的类,yuheng0 和 yuheng1 ,他们都实现了say接口,并且重写了say方法。下面要通过请求k1 k2 获取yuheng0 和 yuheng1类的bean对象。
注意,要记得加上Component注解 交给IOC容器管理他们
这两个类的具体内容如下
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class yuheng0 implements say{
public void say(){
System.out.println("yuheng0");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "k1 to string";
}
}
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class yuheng1 implements say{
public void say(){
System.out.println("yuheng1");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "k2 to string";
}
}
package com.example.demo;
public interface say {
void say();
}
下面是配置类,可以这么写配置来读取自定义配置的信息。这边的map是string string类型的,也就是单纯的把配置类的信息以String的形式读到map里面
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Map;
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "login-type-config") // 注意要对应
public class LoginTypeConfig {
private Map<String,String> types;
public Map<String, String> getTypes() {
return types;
}
public void setTypes(Map<String, String> types) {
this.types = types;
}
}
最后就是最关键的逻辑,实现ApplicationContextAware接口,他可以根据名称从ioc容器中取出对应的bean
这次我们自定义的map类型是string 和 say。根据名称拿到对应的bean对象,也就是yuheng0和yuheng1的对象。放到自定义的map里面。在请求test的时候,从map中拿出已经准备好的bean对象就可以了。
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@RestController
public class demo implements ApplicationContextAware {
@Autowired
private LoginTypeConfig loginTypeConfig;
private static Map<String,say> res = new HashMap<>();
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
loginTypeConfig.getTypes().forEach((k, v) -> {
res.put(k, (say)applicationContext.getBean(v));
});
}
@GetMapping("/test")
public say test(String type)
{
say s = res.get(type);
System.out.println(s.toString());
s.say();
return s;
}
}