某次在Uniapp群看到有人问uniapp如何操作dom元素。
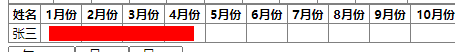
他想对这张表标红的区域,做dom元素获取,因为产品想让红色色块点击时,成为可编辑,渲染1~4月份之间的行程安排。
于是,有小伙伴说让他用position定位这里,点击时使红色色块层级抬高,弄个input上去。
但提问的小伙伴并没有决定这么做,随后不了了之。
在初步自学了一段时间React后,我觉得可以试一下用React实现这种效果。
以下图二为练习之作,实际上对应的月份编辑已经实现
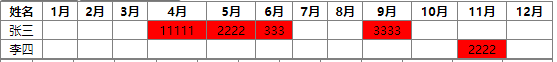
如果要写成如图1那种展示和编辑,就需要td里加入div容器并对其绝对定位
而相应公式了我粗略的整理了一下,并附上
<td className='sTh'>
{/* 做判断,循环时得到的月和次月的做比较,如果次月依旧属于其中,则继续,直到次月不在算入规划中 */}
{/* 默认 1个月为 width 90 * 1 + '%' right:'-5%' */}
{/* 那么 如果2月份也是 width 90 * 2 + '%' right:'-90%' */}
{/* 那么 如果3月份也是 width 90 * 3 + '%' right:'-185%' -85为一刻度,初始-5% */}
{/* 默认右侧偏移量是 100*1 - 5% *1 */}
{/* 新增1个单位 等于 100*2 - 5% *2 */}
{/* 新增2个单位 等于 100*3 - 5% *3 */}
{/* (item.name, index + 1) */}
<div className='sPo' style={{ width: 90 * 4 + '%', right: '-280%' }}
contentEditable={true}
suppressContentEditableWarning={true}
onBlur={() => handleEdit}
ref={editRef}>
{/* <INput /> */}
</div>
</td>
具体做法,其实已经不远。
感兴趣的小伙伴可以体验一下,当然,如果发现有什么地方存在问题或缺陷bug,欢迎指正。
table 无状态组件
import React, { useState, useRef } from 'react';
const Table = () => {
const [data, setData] = useState([{ name: '张三', li: [4, 9, 5, 6] }, { name: '李四', li: [11] }]);
const editRef = useRef('null');
// 被操作的名字
// 被操作的月份
// 被操作的值
const handleEdit = (name, month, e) => {
const newData = [...data];
const item = newData.find((item) => item.name === name);
item.li[month] = parseInt(e.target.innerText);
setData(newData);
};
const renderTable = () => {
const months = ['1月', '2月', '3月', '4月', '5月', '6月', '7月', '8月', '9月', '10月', '11月', '12月'];
const tableData = [];
// 添加表头
const headerRow = [<th key="name" className='sTh'>姓名</th>];
months.forEach((month) => {
headerRow.push(<th key={month} className='sTh'>{month}</th>);
});
tableData.push(<tr key="header" className='sTh'>{headerRow}</tr>);
// 添加数据行
data.forEach((item) => {
const dataRow = [<td key="name" className='sTh'>{item.name}</td>];
months.forEach((month, index) => {
if (item.li.includes(index + 1)) {
const value = item.li[index + 1] || '';
dataRow.push(
<td
key={month}
style={{ backgroundColor: 'red' }}
contentEditable={true}
suppressContentEditableWarning={true}
onBlur={(e) => handleEdit(item.name, month, e)}
ref={editRef}
className='sTh'
>
{value}
</td>
);
} else {
dataRow.push(<td key={month} className='sTh'></td>);
}
});
tableData.push(<tr key={item.name} className='sTh'>{dataRow}</tr>);
});
return tableData;
};
return (
<table className='sTab'>
<tbody>{renderTable()}</tbody>
</table>
);
};
</details>
.sTab {
border-collapse: collapse;
border: 1px solid gray;
width: 100%;
text-align: center;
font-size: 0.28rem;
}
/*
1. separate:默认值,边框会被分开,不会忽略border-spacing 和 empty-cells 属性。
2. collapse:如果可能,边框会合并为一个单一的边框。会忽略 border-spacing 和 empty-cells 属性。
3. inherit:规定应该从父元素继承border-collapse 属性的值
*/
.sTh {
border: 1px solid gray;
border-top: none;
border-left: none;
position: relative;
}
.sPo{
height: 15px;
position: absolute;
top: 2px;
right: -2%;
z-index: 10;
width: 100%;
background: red;
}
/*
contenteditable 编辑时带来的黑框
*/
[contenteditable]:focus {
outline: none;
}