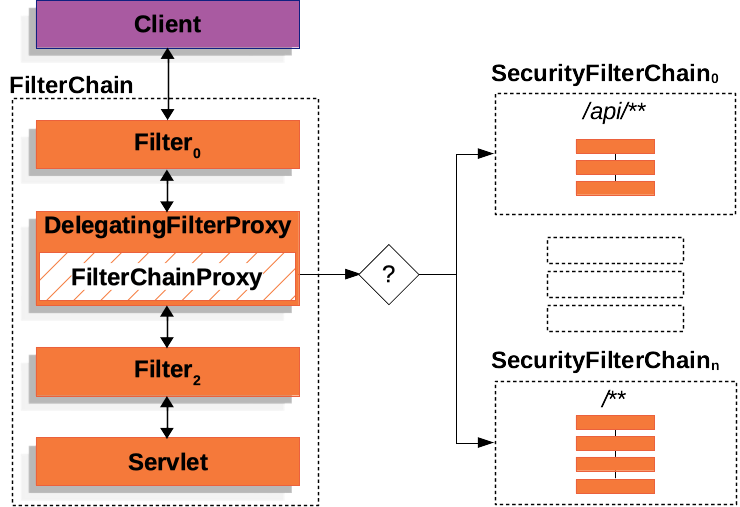
ObjectStream
ObjectOutputStream
用于将属性和内容保存到文件中,保存数据类型和值,即序列化,该流为处理流
static和transient修饰的属性无法序列化,切被序列化的类必须实现Serializable接口,该类的属性中如果有类这个类也必须实现该接口.
package com.cn.file;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.*;
public class MyObjectStream {
@Test
public void test(){
//序列化,将带属性的内容存入文件,必须实现Serializable
// 接口的对象才能被写入
String filePath="F:\\y\\file01.txt";
ObjectOutputStream os =null;
Dog dog1=new Dog(4,"哈哈");
try {
os=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(filePath));
os.writeByte(10);
os.writeChar('a');
os.writeInt(100);
os.writeUTF("改革春风abc");
os.writeObject(dog1);
os.writeObject(new Dog(6,"嘿嘿"));
System.out.println("序列化完成");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
ObjectInputStream
用于反序列化,将文件内容读取出来.
package com.cn.file;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
public class MyObjectStream2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
String filePath="F:\\y\\file01.txt";
ObjectInputStream is=new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filePath));
//反序列化时顺序要和写入顺序一致,不然乱码
System.out.println(is.readByte());
System.out.println(is.readChar());
System.out.println(is.readInt());
System.out.println(is.readUTF());
Object dog=is.readObject();
System.out.println(dog.getClass());
System.out.println(dog.toString());
is.close();
}
}