Rust 依赖包安装
-
在系统中设置path
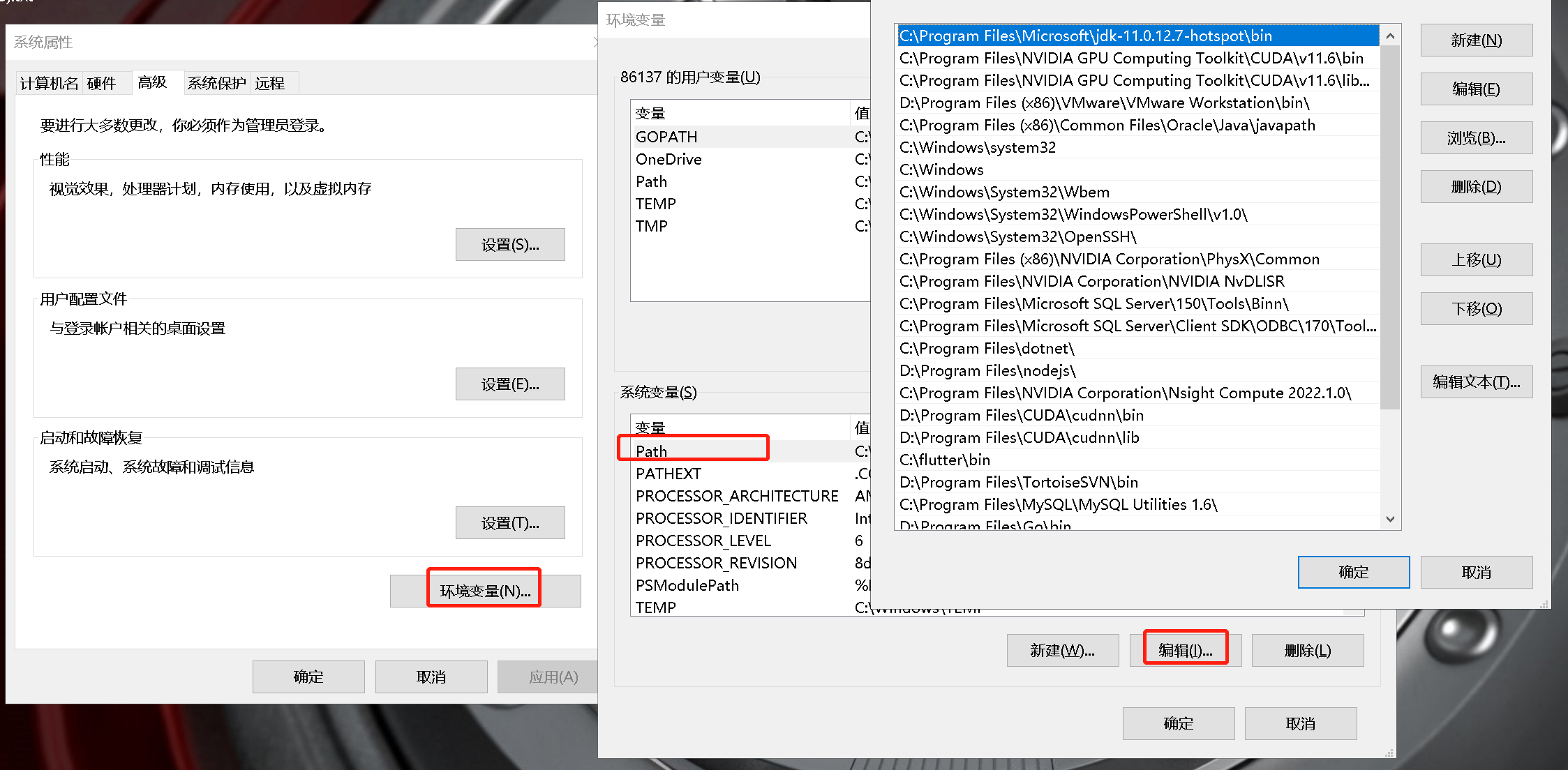
-
使用命令判断是否安装成功
rustc --version
cargo --version -
创建项目
cargo new 项目名称
-
编译
cargo build
-
运行
cargo run
Rust 环境搭建(vs code)
-
安装vs code
-
下载 Rust插件(插件工具栏搜索Rust插件)
-
搜索rust-analyzer 插件
-
创建Rust工作空间
-
创建cargo new 项目名称后,在项目名称文件夹下运行cmd 输入code . 打开vs code可直接使用
fn main() { println!("Hello, world!"); } -
配置环境变量
{ "rust.mode": "rls", "rust.cargoHomePath": "%CARGO_HOME%", "rust.cargoPath":"%RUSTBINPATH%\\cargo.exe", "rust.racerPath":"%RUSTBINPATH%\\racer.exe", "rust.rls":"%RUSTBINPATH%\\rls.exe", "rust.rustfmtPath":"%RUSTBINPATH%\\rustfmt.exe", "rust.rustup":"%RUSTBINPATH%\\rustup.exe", "rust.rustLangSrcPath": "%RUST_SRC_PATH%", "rust.executeCargoCommandInTerminal": true, "workbench.statusBar.feedback.visible": false, "rust.actionOnSave": "build", "debug.allowBreakpointsEverywhere": true, "rust-client.disableRustup": true, } -
设置编译环境
{ // Use IntelliSense to learn about possible attributes. // Hover to view descriptions of existing attributes. // For more information, visit: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387 "version": "0.2.0", "configurations": [ { "name": "rust", "type": "cppvsdbg", "request": "launch", //"program": "enter program name, for example ${workspaceFolder}/a.exe", "program": "./target/debug/Output.exe", "args": [], "stopAtEntry": false, "cwd": "${workspaceFolder}", "environment": [], "externalConsole": true, } ] } -
运行结果如下
Hello, world!
注释方式
- 单行注释 ( \\ )
- 范围注释 (\* 开始 结束*\ )
基础类型
-
基本类型 整型(有符号和无符号)和char(字符型)
有符号 i8 i16 i32 i128 和 isize 例如 let _number: i8 = 100;
无符号 u8 u16 u32 u128 和 usize 例如 let _number: u8 = 100;
char ansi码和unicode码来识别的
整型和char互转
let _number = 100; println!("{}", _number as u8 as char) 输出为 d -
可通过std标准库来获得类型最大值和最小是
println!(" i8 between {} and {}", std::i8::MIN, std::i8::MAX); println!(" u8 between {} and {}", std::u8::MIN, std::u8::MAX); println!(" i128 between {} and {}", std::i128::MIN, std::i128::MAX); println!(" u128 between {} and {}", std::u128::MIN, std::u128::MAX); -
char长度问题 len和count
// len()为字节的大小 chars().count() 为汉字或英文的长度 let slice = "中国人"; println!("Slice is {} bytes and Word is {}", slice.len(), slice.chars().count());返回结果:Slice is 12 bytes and Word is 3
-
指定一个类型
let _number = 10; // 编译器可能会认为是i16 let _number: u8 = 10; // 告知编译器该变量为u8 let _number = 10u8; // 与上一条等价 let _number = 10_u8; // 与上一条等价 let _number = 1____0___u8 //同上 _只是方便阅读 -
浮点数
let my_float:f32 = 8.5 // 设置为32位浮点数
let my_float = 8.0; // 编译器认为类型是f64 let second_float:f32 = 83.0; // f32无法与f64直接相加,类型不一致 let third_float = my_float + second_float as f64 -
字符串 String和&str
-
相同点
都是UTF8
-
不同点
&str 比 String快, String是指针,数据在堆上
&str 知道大小(str动态,因此加了&),String不知道
创建方式不同
let name= "name"; 为&str let string_name = String::form("this is name"); 为String let other_name = "this is name".to_string() 将&str转换为String let together = format!("together {} and {}", "a", "b"); together为String
-
-
into()用法
必须声明来判断into创建的类型 let my_string: String = "this is world".into(); 创建为String -
类型可变 let mut -------不能改变类型
如果直接输入let number = 10 类似于 const int number = 10,无法再次复制,因此需要加上mut
-
遮蔽
如果不存在{}时,相同的变量名以最新声明的为准
函数
-
带返回参数的函数
fn nunber()-> i32{ 8 //没有冒号 } fn main(){ println!("number is {}", number()); } -
带参函数
fn sumNumber(number_one: i32, number_tow: i32){ let result = number_one + number_tow; println!("{} add {} is {}", number_one, number_tow, result); } fn main(){ sumNumber(8, 9); let num_one = 1; let num_tow = 4; sunNumber(num_one, num_tow); } -
带参返回函数
fn sumNumber(number_one: i32, number_tow: i32)-> i32{ let result = number_one + number_tow; retuls // 注意,没有分号 } fn main(){ let result_number = sunNumber(10, 9); }
打印信息
-
println!("{}", 1); // 普通打印
-
println!("{:?}", 1): // Debug方式打印 打印字节数
-
println!("{:#?}", 1); // 漂亮打印
-
println!("{:p}", &number); //打印指针
let number = 9; let number_ref = &number; println!("{:p}", number_ref); -
println!("{:X}", 'H' as u32) 转为Unicode数字再打印
-
二进制、八进制和十六进制 注意16进制和Unicode的区别(x和X)
let number = 555; println!("Binary: {:b}, octal: {:o}, hexadecimal: {:x}", number, number, number); -
循环打印
{variable:padding alignment minimum.maximum} variable:变量名,如果不用变量则可使用: padding:填充字符 alignment:对齐方式 < 左 ^中 >右 minimum:最小长度 maximum:最大长度 println!("{:-^11}", "A"); 输出结果:-----A----- let title = "TODAY'S NEWS"; println!("{:-^30}", title); // no variable name, pad with -, put in centre, 30 characters long let bar = "|"; println!("{: <15}{: >15}", bar, bar); // no variable name, pad with space, 15 characters each, one to the left, one to the right let a = "SEOUL"; let b = "TOKYO"; println!("{city1:-<15}{city2:->15}", city1 = a, city2 = b); // variable names city1 and city2, pad with -, one to the left, one to the right 结果: ---------TODAY'S NEWS--------- | | SEOUL--------------------TOKYO -
\ 为转义
-
忽略转义
println(r#"\r\n "find file c:\files\file.txt"");
-
打印:#
println!(r##"write one#"##) result: write one#
println!(r###"write one#, and another one #"###) result:write one#, and another one #
栈、堆和指针
-
速度:栈>堆
-
栈
指定大小的可以放在栈中,不定的可以通过指针找到堆中的数值
-
堆
存放数据,栈可通过指针地址查找数据
-
指针 使用&
多层指针嵌套 let my_number = 15; // This is an i32 let single_reference = &my_number; // This is a &i32 let double_reference = &single_reference; // This is a &&i32 let five_references = &&&&&my_number; // This is a &&&&&i32
checked_add
-
u16::checked_add(251, 8).unwrap();
/* checked_add的方式有两种 第一种为u16::checked_add(数值,数值),相加 第二种类型直接调用checked_add() checked_*:返回的类型是Option<_>,当出现溢出的时候,返回值是None; saturating_*:返回类型是整数,如果溢出,则给出该类型可表示范围的“最大/最小”值; wrapping_*:直接抛弃已经溢出的最高位,将剩下的部分返回 */ let i = 100_i8; println!("checked {:?}", i.checked_add(i)); println!("saturating {:?}", i.saturating_add(i)); println!("wrapping {:?}", i.wrapping_add(i)); /* unwrap()方法源代码如下 pub fn unwrap(self) -> T { match self { Ok(t) => t, Err(e) => unwrap_failed("called `Result::unwrap()` on an `Err` value", e), } } 相关类型:unwrap_or 、 unwrap_or_else 或 unwrap_or_default 。 不建议使用,因为会出现Panics(程序终止) */ let x:Option<&str> = None; assert_eq!(x.unwrap(), "air"); // fails
获取数组
-
举例说明
use std::ops::{Range, RangeInclusive}; Range{ start: 1, end: 5 }) // 不包含5 RangeInclusive::new(1, 5) // 包含5 -
数据位置说明
size_of_val("中"), "中".len(), "中".chars().count()
3, 3, 1 -
字符说明
"" 类型是&str
'' char -
中文说明
let _v: () = (); // 定义函数 assert!(size_of_val(&unit) == 0); let c2 = '中'; assert_eq!(size_of_val(&c2),4);