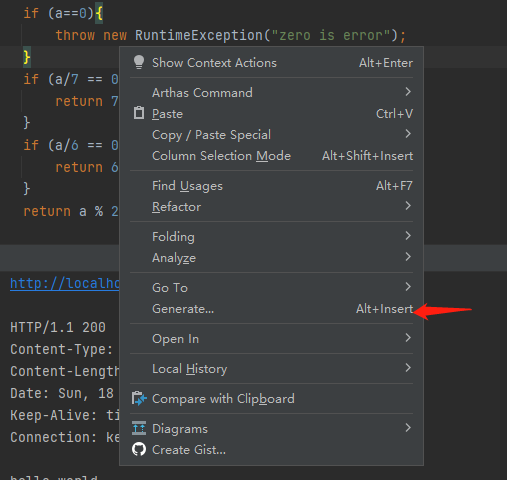
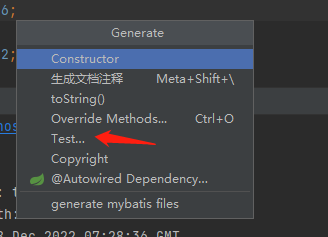
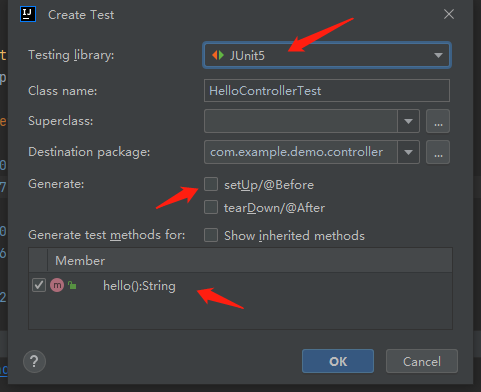
请给我的爱人来一杯mockito.在Java单元测试中,Mockito是一个常见的测试框架。我将在这篇文章中简单介绍一下Mockito的使用。欢迎大家留言讨论
Test Double( 测试替身 )
- Dummy:不包含实作,在该次测试中完全用不上,只是为了满足编译而传入
- Stub: Method只会回传固定值,用来验证状态
- Spy:会记录SUT与DOC之间的行为互动,用来验证行为
- Fake: 会有接近原始物件的行为,但是会以简单的方式来做
- Mock:通过Mocking framework产生,可以快速的做到Dummy,Stub,Spy
为什么要使用Mock
Mock可以就是创建一个虚拟的对象,在测试环境中替换真实的对象,以便我们可以:
- 验证该对象某些方法的调用情况,调用了多少次
- 对这个对象的行为进行定义,来指定返回结构或者特定的动作。
在使用Mock对象时,我们没有对一个方法/行为进行定义,则Mock对象方法就会返回这个方法返回类型的默认值
@Test
void add() {
Random mock = Mockito.mock(Random.class);
System.out.println(mock.nextInt()); // 此处拥有只用返回0,应为返回类型为int, int的默认值为0
Mockito.verify(mock).nextInt();
Mockito.verify(mock, Mockito.times(1)).nextInt();
}
对Mock对象的方法、行为进行定义,俗称打桩
@Test
void add2() {
Random mock = Mockito.mock(Random.class);
Mockito.when(mock.nextInt()).thenReturn(100); // 这就是打桩
int nextInt = mock.nextInt();// 此时每次都会返回100
Mockito.verify(mock).nextInt(); // 判断这个方法有没有调用过
Mockito.verify(mock, Mockito.times(1)).nextInt(); // 判断这个方法调用的具体次数
Assertions.assertEquals(100,nextInt); // 断言
}
注解实现
@Mock: mock注解。在使用mock注解时,一定要使用MockitoAnnotations.openMocks来开启Mock注解
@Mock
private Random random;
@Test
void add3() {
MockitoAnnotations.openMocks(this); // 开启Mock注解
Mockito.when(random.nextInt()).thenReturn(100); // 这就是打桩
int nextInt = random.nextInt();// 此时每次都会返回100
Mockito.verify(random).nextInt(); // 判断这个方法有没有调用过
Mockito.verify(random, Mockito.times(1)).nextInt(); // 判断这个方法调用的具体次数
Assertions.assertEquals(100,nextInt); // 断言
}
还有@BeforeEach和@AfterEach, 用于测试前准备和结束收尾
Spy对象和@Spy注解
spy()和mock()方法不同的是:
- 被spy的对象会走真实的方法,而Mock对象不会
- spy方法的参数是对象实例,而mock参数是class实例
@Spy
private Random randomSpy; // 通过注解实现
@Test
void add4(){
Random spy = Mockito.spy(new Random()); // 通过new实例实现
int nextInt = randomSpy.nextInt();
System.out.println(nextInt);
Mockito.when(randomSpy.nextInt()).thenReturn(100); // 对spy对象打桩后,之后nextInt返回都是100
for(int i=0; i < 10; i++){
System.out.println(randomSpy.nextInt());
}
Mockito.when(randomSpy.nextInt()).thenCallRealMethod(); // 再走真实的方法
}
Mock的实际应用
其实在mock的实际应用中,代码的规范才能更好的写出好的单元测试
例如:
void test1(){
RestTemplateService restTempServ = new RestTempServImpl();
String ans = restTempServ.sendMessage("ok");
FileService fileService = new FileServiceImpl();
fileService.saveFile("Hello");
DBservice dbServ = new DBServImpl();
dbServ.save(ans);
System.out.println("test1");
}
这样的一段代码,我们就很难写出很好的UT,其他服务的对象全部都new在代码中了。最好是写的时候就要考虑的UT的存在。此处,我们就需要对代码进行重构;
@Autowired
private RestTemplateService restTemplateService;
@Autowired
private FileService fileService;
@Autowired
private DBservice dBservice;
void test2(){
String ans = restTemplateService.sendMessage("ok");
fileService.saveFile("Hello");
dBservice.save(ans);
System.out.println("test1");
}
我们把其他服务的对象通过DI注入到对象中。
这时候,我们UT测试:
class DemoTest2Test {
@InjectMocks // 将剩下的Mock对象自动注册到该对象中
@Spy
private DemoTest2 demoTest2; // 这是需要测试的对象
@Mock
private RestTemplateService restTemplateService;
@Mock
private FileService fileService;
@Mock
private DBservice dBservice;
@BeforeEach
void before(){
MockitoAnnotations.openMocks(this); // 开启Mock注解
}
@Test
void test2() {
}
}
Mock实战
需要测试的方法
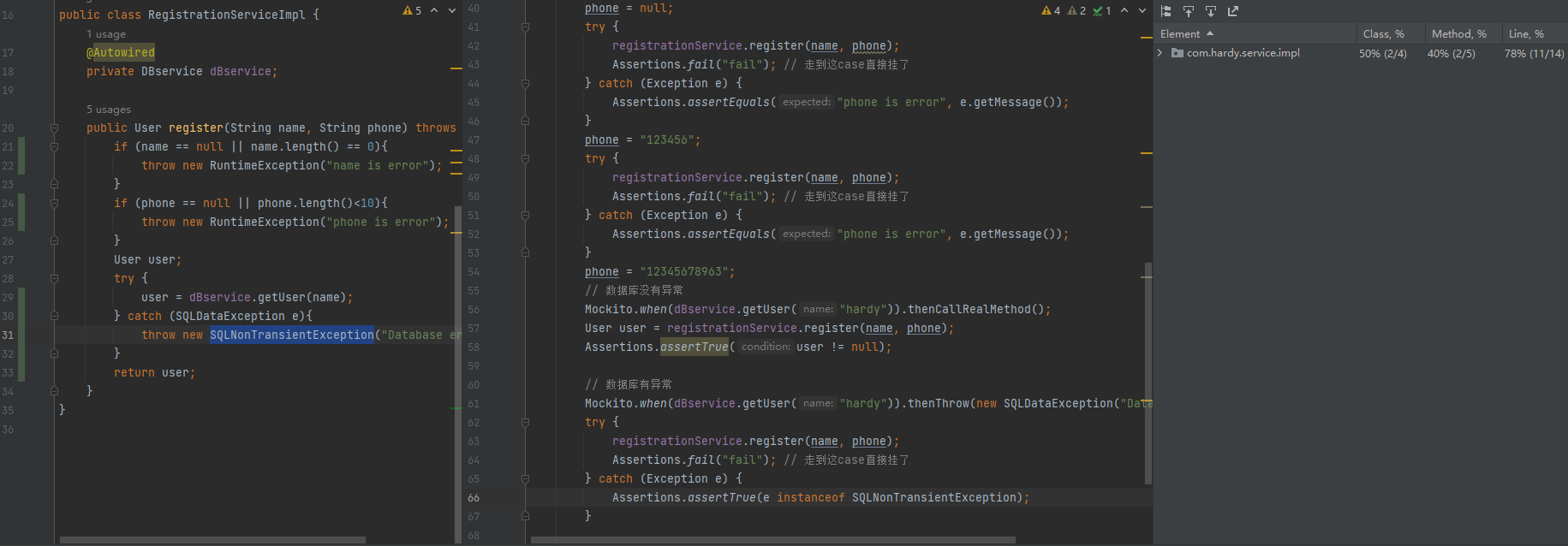
public class RegistrationServiceImpl {
@Autowired
private DBservice dBservice;
public User register(String name, String phone) throws Exception{
if (name == null || name.length() == 0){
throw new RuntimeException("name is error");
}
if (phone == null || phone.length()<10){
throw new RuntimeException("phone is error");
}
User user;
try {
user = dBservice.getUser(name);
} catch (SQLDataException e){
throw new SQLNonTransientException("Database error");
}
return user;
}
}
UT代码
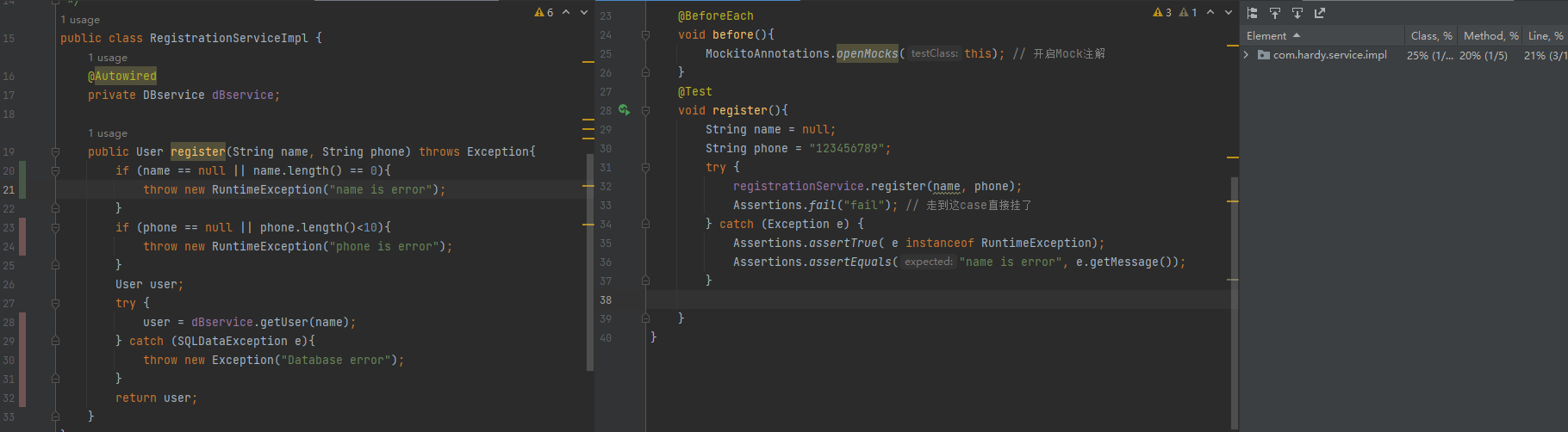
class RegistrationServiceImplTest {
@InjectMocks // 将剩下的Mock对象自动注册到该对象中
@Spy
private RegistrationServiceImpl registrationService; // 这是需要测试的对象
@Mock
private DBServImpl dBservice;
@BeforeEach
void before(){
MockitoAnnotations.openMocks(this); // 开启Mock注解
}
@Test
void register() throws Exception {
String name = null;
String phone = "123456789";
try {
registrationService.register(name, phone);
Assertions.fail("fail"); // 走到这case直接挂了
} catch (Exception e) {
Assertions.assertTrue( e instanceof RuntimeException);
Assertions.assertEquals("name is error", e.getMessage());
}
name = "hardy";
phone = null;
try {
registrationService.register(name, phone);
Assertions.fail("fail"); // 走到这case直接挂了
} catch (Exception e) {
Assertions.assertEquals("phone is error", e.getMessage());
}
phone = "123456";
try {
registrationService.register(name, phone);
Assertions.fail("fail"); // 走到这case直接挂了
} catch (Exception e) {
Assertions.assertEquals("phone is error", e.getMessage());
}
phone = "12345678963";
// 数据库没有异常
Mockito.when(dBservice.getUser("hardy")).thenCallRealMethod();
User user = registrationService.register(name, phone);
Assertions.assertTrue(user != null);
// 数据库有异常
Mockito.when(dBservice.getUser("hardy")).thenThrow(new SQLDataException("Database is error"));
try {
registrationService.register(name, phone);
Assertions.fail("fail"); // 走到这case直接挂了
} catch (Exception e) {
Assertions.assertTrue(e instanceof SQLNonTransientException);
}
}
}
具体操作
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mockito/mockito-core -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mockito</groupId>
<artifactId>mockito-core</artifactId>
<version>4.3.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.junit.jupiter/junit-jupiter-api -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId>
<version>5.8.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>