目录
本文使用的环境: Bash 4.2.46
bash启动时会执行一系列脚本, 具体要执行哪些启动文件, 这和bash的类型有关: 是否为交互式(interactive)的shell, 是否为登录式(login)的shell
1. 交互式shell/非交互式shell
1.1 如何启动一个交互式shell/非交互式shell
- 日常使用ssh登录的shell是交互式shell
- 图形化界面下打开的terminal也是交互式shell
- 通过
bash script.sh或./script.sh执行脚本时, 会创建一个子shell来执行此脚本, 此时的子shell为非交互式shell - 通过ssh远程执行命令的shell为非交互式shell
1.2 如何判断是否为交互式shell
$-会输出set设置的一些选项, 输出结果结果中的i表示interactive(但不能通过set设置是否为交互式)
# 脚本中判断是否为交互式shell
case "$-" in
*i*) echo 'This shell is interactive' ;;
*) echo 'This shell is not interactive' ;;
esac
# 此时为交互式shell
$ echo $-
himBHs
# 执行脚本时创建的子shell为非交互式shell
$ cat script.sh
echo "$-"
$ bash script.sh
hB
在非交互式shell不会设置PS1, 所以通过PS1是否有值判断也是可行的
if [ -z "$PS1" ]; then
echo 'This shell is not interactive'
else
echo 'This shell is interactive'
fi
2. 登录式shell/非登录式shell
2.1 如何启动一个登录式shell/非登录式shell
- 通过
bash -l或su -l命令启动的为登录式shell - 通过ssh登录的shell为登录式shell
- 通过ssh远程执行命令的shell为非登录式shell
- 图形化界面下启动的"terminal"默认为非登录式的, 但是可以更改为登录式shell
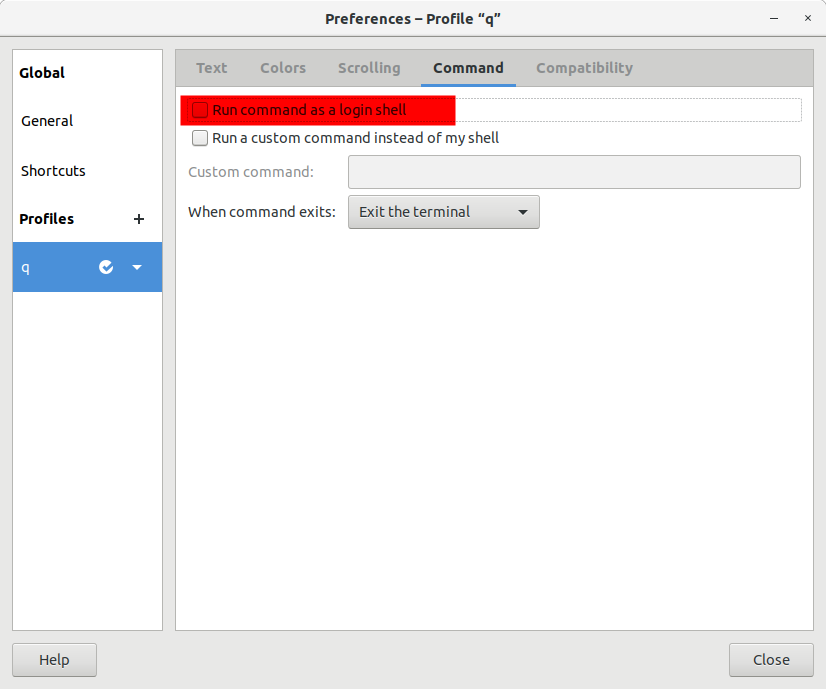
2.2 如何判断是否为登录式shell
可通过shopt命令来查看是否为登录式shell, 也可以通过此命令来转换登录式/非登录式shell
$ shopt login_shell
login_shell off
3. 启动文件
了解了什么是交互式/登录式shell之后, 我们来看下这4种情况下shell的初始化文件
3.1 测试方法
涉及到的文件主要有: /etc/profile, ~/.profile, ~/.bash_profile, ~/.bash_login, ~/.bashrc
将echo [/etc/profile]添加到/etc/profile的第一行(其他文件同理), 根据每次登录服务器时的输出就能看到哪些文件被执行了
3.2 交互登录shell
交互登录式shell初始化的文件为:
- /etc/profile
- ~/.bash_profile, ~/.bash_login, and ~/.profile 这三个文件只会执行其中一个, 找到其中一个别的就不执行了, 优先级从前往后递减
通过ssh的方式登录即可得到交互登录式shell
$ ssh wbourne@192.168.0.101
[/etc/profile]
[~/.bash_profile]
[~/.bashrc]
再来验证~/.bash_profile, ~/.bash_login, and ~/.profile这三个文件的优先级
将~/.bash_profile改名为~/.bash_profile.bak, 再次登录服务器, 可以看到, ~/.bash_profile没有被执行, 取而代之的是~/.bash_login
$ ssh wbourne@192.168.0.101
[/etc/profile]
[~/.bash_login]
执行完成之后, 为了不影响后续测试, ~/.bash_profile.bak改回~/.bash_profile
3.3 交互非登录shell
交互非登录式shell初始化的文件为:
- ~/.bashrc
通过su命令切换用户即可得到交互非登录式shell
$ ssh root@192.168.0.101
$ su wbourne
[~/.bashrc]
通过su切换用户后, 按下Tab键发现自动补全用不了, 是因为/etc/profile中有以下一段脚本, 而自动补全与/etc/profile.d中的脚本有关
可以将这一段添加到~/.bashrc文件中, 就可以使交互式shell都能够自动补全, 至于为什么, 会在4.2 ~/.bashrc中讲到
if [ -d /etc/profile.d ]; then
for i in /etc/profile.d/*.sh; do
if [ -r $i ]; then
. $i
fi
done
unset i
fi
3.4 非交互非登录shell
非交互非登录式shell初始化的文件为:
- 查找
$BASH_ENV变量并执行, 就像if [ -n "$BASH_ENV" ]; then . "$BASH_ENV"; fi一样
bash xxx.sh所创建用来执行脚本的子shell为非登录非交互式shell
# 登录服务器时的shell是交互登录式shell
$ ssh wbourne@192.168.0.101
[/etc/profile]
[~/.bash_profile]
[~/.bashrc]
# 编写一个脚本并执行, 执行脚本时创建的子shell才是非交互非登录shell
# 此处只有脚本本身的输出, 没有任何初始化文件被执行
$ cat script.sh
echo "$-"
echo "$BASH_ENV"
shopt login_shell
$ bash script.sh
hB
login_shell off
设置$BASH_ENV变量, 再次测试, 可以看到, ~/.bashrc被执行
$ export BASH_ENV='~/.bashrc'
$ bash script.sh
[~/.bashrc]
hB
~/.bashrc
login_shell off
测试完之后执行unset BASH_ENV删除BASH_ENV变量, 以免影响带后续测试
3.5 非交互登录shell
非交互登录式shell初始化的文件为:
- /etc/profile
- ~/.bash_profile, ~/.bash_login, and ~/.profile 同上, 三取其一
- 查找
$BASH_ENV变量并执行, 就像if [ -n "$BASH_ENV" ]; then . "$BASH_ENV"; fi一样
在bash xxx.sh的基础上加上-l选项可得到登录非交互式shell
$ cat script.sh
echo "$-"
echo "$BASH_ENV"
shopt login_shell
$ bash -l script.sh
[/etc/profile]
[~/.bash_profile]
[~/.bashrc]
hB
login_shell on
再验证下$BASH_ENV. 注意, .bashrc输出了两次, 4.2 ~/.bashrc会讲到为什么
$ export BASH_ENV='~/.bashrc'
$ bash -l script.sh
[/etc/profile]
[~/.bash_profile]
[~/.bashrc]
[~/.bashrc]
hB
~/.bashrc
login_shell on
4. 其他
4.1 /etc/bash.bashrc与/etc/bashrc
大部分发行版还会涉及/etc/bash.bashrc与/etc/bashrc这两个文件, 例如Ubuntu 18.04 Desktop的/etc/profile文件中有. /etc/bash.bashrc的语句, CentOS 7 Server的~/.bashrc文件中有. /etc/bashrc的语句
4.2 ~/.bashrc
上述例子中, 只有交互非登录shell才会调用~/.bashrc, 但是其他例子的输出也包含了~/.bashrc, 甚至有的执行了两次, 这是因为:
一般的发行版中, ~/.profile文件中一般都有. ~/.bashrc的语句, 以此来保证无论是登录式shell还是非登录式shell, ~/.bashrc都会被执行. 换句话说, 只要是交互式shell, ~/.bashrc都会被执行





.png)