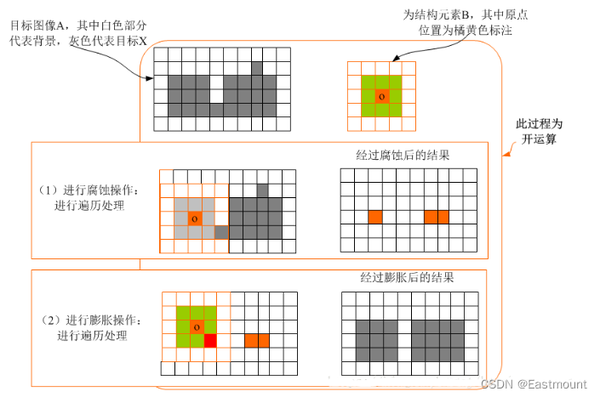
哈希算法经常会被用到,比如我们Go里面的map,Java的HashMap,目前最流行的缓存Redis都大量用到了哈希算法。它们支持把很多类型的数据进行哈希计算,我们实际使用的时候并不用考虑哈希算法的实现。而其实不同的数据类型,所使用到的哈希算法并不一样。
DJB
下面是C语言实现。初始值是5381,遍历整个串,按照hash * 33 +c的算法计算。得到的结果就是哈希值。
unsigned long
hash(unsigned char *str)
{
unsigned long hash = 5381;
int c;
while (c = *str++)
hash = ((hash << 5) + hash) + c; /* hash * 33 + c */
return hash;
}
里面涉及到两个神奇的数字,5381和33。为什么是这两个数?我还特意去查了查,说是经过大量实验,这两个的结果碰撞小,哈希结果分散。
还有一个事情很有意思,乘以33是用左移和加法实现的。底层库对性能要求高啊。
DJB 在 Redis中的应用
在Redis中,它被用来计算大小写不敏感的字符串哈希。
static uint32_t dict_hash_function_seed = 5381; /* And a case insensitive hash function (based on djb hash) */ unsigned int dictGenCaseHashFunction(const unsigned char *buf, int len) { unsigned int hash = (unsigned int)dict_hash_function_seed; while (len--) hash = ((hash << 5) + hash) + (tolower(*buf++)); /* hash * 33 + c */ return hash; }
算法和之前的一样,只是多了一个tolower函数把字符转成小写。
Java 字符串哈希
看了上面的再看Java内置字符串哈希就很有意思了。Java对象有个内置对象hash,它缓存了哈希结果,如果当前对象有缓存,直接返回。如果没有缓存,遍历整个字符串,按照hash * 31 + c的算法计算。
public int hashCode() {
int h = hash;
if (h == 0 && value.length > 0) {
char val[] = value;
for (int i = 0; i < value.length; i++) {
h = 31 * h + val[i];
}
hash = h;
}
return h;
}
和DJB相比,初始值从5381变成了0,乘的系数从33变成了31。
FNV
字符串每一位都看成是一个数字,32位的话看成是16777169进制的数字,计算当前串的哈希值就是在把当前串转成10进制。
const primeRK = 16777619 // hashstr returns the hash and the appropriate multiplicative // factor for use in Rabin-Karp algorithm. func hashstr(sep string) (uint32, uint32) { hash := uint32(0) for i := 0; i < len(sep); i++ { hash = hash*primeRK + uint32(sep[i]) } var pow, sq uint32 = 1, primeRK for i := len(sep); i > 0; i >>= 1 { if i&1 != 0 { pow *= sq } // 只有32位,超出范围的会被丢掉 sq *= sq } return hash, pow }
这个算法的厉害之处在于他可以保存状态。比如有个字符串ab,它的哈希值是a*E+b=HashAB,如果计算bc的哈希值,可以利用第一次计算的结果(HashAB-a*E)*E+c=HashBC。这么一个转换例子里是两个字符效果不明显,如果当前串是100个字符,后移一位的哈希算法性能就会快很多。
在Golang里面字符串匹配算法查找用到了这个。
Thomas Wang’s 32 bit Mix Function
前面说的都是字符串的哈希算法,这次说整数的。
public int hash32shift(int key) { key = ~key + (key << 15); // key = (key << 15) - key - 1; key = key ^ (key >>> 12); key = key + (key << 2); key = key ^ (key >>> 4); key = key * 2057; // key = (key + (key << 3)) + (key << 11); key = key ^ (key >>> 16); return key; }
Redis对于Key是整数类型时用了这个算法。
Murmur
就纯哈希算法来说,这个算法算是综合能力不错的算法了。碰撞小、性能好。
Hash Lowercase Random UUID Numbers ============= ============= =========== ============== Murmur 145 ns 259 ns 92 ns 6 collis 5 collis 0 collis FNV-1a 152 ns 504 ns 86 ns 4 collis 4 collis 0 collis FNV-1 184 ns 730 ns 92 ns 1 collis 5 collis 0 collis▪ DBJ2a 158 ns 443 ns 91 ns 5 collis 6 collis 0 collis▪▪▪ DJB2 156 ns 437 ns 93 ns 7 collis 6 collis 0 collis▪▪▪ SDBM 148 ns 484 ns 90 ns 4 collis 6 collis 0 collis** SuperFastHash 164 ns 344 ns 118 ns 85 collis 4 collis 18742 collis CRC32 250 ns 946 ns 130 ns 2 collis 0 collis 0 collis LoseLose 338 ns - - 215178 collis
一般在分布式系统中用的比较多。对于一个Key做哈希,把不同的请求转发到不同的服务器上面。
推荐一个Go的实现。
CRC32
CRC32的哈希碰撞和murmur的差不多,但是CRC32可以使用CPU的硬件加速实现哈希提速。
在Codis上就使用了这个哈希算法做哈希分片,SlotId= crc32(key) % 1024。
Codis使用Go语言实现,CRC32算法直接用了Go的原生包hash/crc32。这个包会提前判断当前CPU是否支持硬件加速:
func archAvailableIEEE() bool { return cpu.X86.HasPCLMULQDQ && cpu.X86.HasSSE41 }
memhash
Go语言内置的哈希表数据结构map,也是一个哈希结构,它内置的哈希算法更讲究。
这里用到的哈希算法是memhash,源代码在runtime/hash32.go里面。它基于谷歌的两个哈希算法实现。大家有兴趣的可以去研究下具体实现。
// Hashing algorithm inspired by // xxhash: https://code.google.com/p/xxhash/ // cityhash: https://code.google.com/p/cityhash/
memhash在具体实现时也用到了硬件加速。如果硬件支持,会用AES哈希算法。如果不支持,才会去用memhash。
func memhash(p unsafe.Pointer, seed, s uintptr) uintptr { if GOARCH == "386" && GOOS != "nacl" && useAeshash { return aeshash(p, seed, s) } h := uint32(seed + s*hashkey[0])