引言
设置两个窗口(线程),交替卖出100张票,一个线程卖寄数,一个线程卖偶数,要求交替卖出,最后数据 1 ,2,,3,4,5,6......100
1 /** 2 * @ClassName AlternatePrintThread 3 * @Description 设计两个线程,卖出1-100张票,一个线程打印奇数张,另一个线程打印偶数张,要求交替打印。 最后输出123……100 4 * @Author zhao's'qing 5 * @Date 2022/11/10 15:21 6 * @Version 1.0 7 **/ 8 public class AlternatePrintThread { 9 10 static final Object obj = new Object(); 11 private static int flag = 0; 12 13 private static volatile boolean flag2 = false; 14 15 private static Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 16 private static Condition condition = lock.newCondition(); 17 private static boolean flag3 = false; 18 19 public static void main(String[] args) { 20 AlternatePrintThread apt = new AlternatePrintThread(); 21 apt.test1(); 22 //apt.test2(); 23 //apt.test3(); 24 //apt.test4(); 25 // apt.test5(); 26 27 } 28 }
方法一(Synchronized+共享变量)
解题思路
新建一个对象,并定义一个共享变量。只要flag不为1,线程t2就会阻塞,释放锁资源,所以t1线程先执行,此时flag为0,跳过while判断,然后修改flag为1,打印奇数张票,并唤醒t2,由于flag被改为1,下次循环,t1就会阻塞。t2被唤醒后,t1已经释放了锁资源,所以t2可以获取锁资源,并且flag为1,跳过while循环,修改flag为0,打印偶数张票,唤醒t1。
代码实现:
1 public void test1(){ 2 Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> { 3 synchronized (obj) { 4 for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i += 2) { 5 while (flag != 0) { 6 try { 7 obj.wait(); 8 Thread.sleep(200); 9 } catch (Exception e) { 10 e.printStackTrace(); 11 } 12 } 13 flag = 1; 14 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 卖出第 :" + i +" 张票!"); 15 obj.notify(); 16 17 } 18 } 19 }, "线程A"); 20 21 Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{ 22 synchronized (obj) { 23 for (int i = 2; i <= 10; i += 2) { 24 while (flag != 1) { 25 try { 26 obj.wait(); 27 Thread.sleep(200); 28 } catch (Exception e) { 29 e.printStackTrace(); 30 } 31 } 32 flag = 0; 33 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 卖出第:" + i +" 张票"); 34 obj.notify(); 35 } 36 } 37 },"线程B");
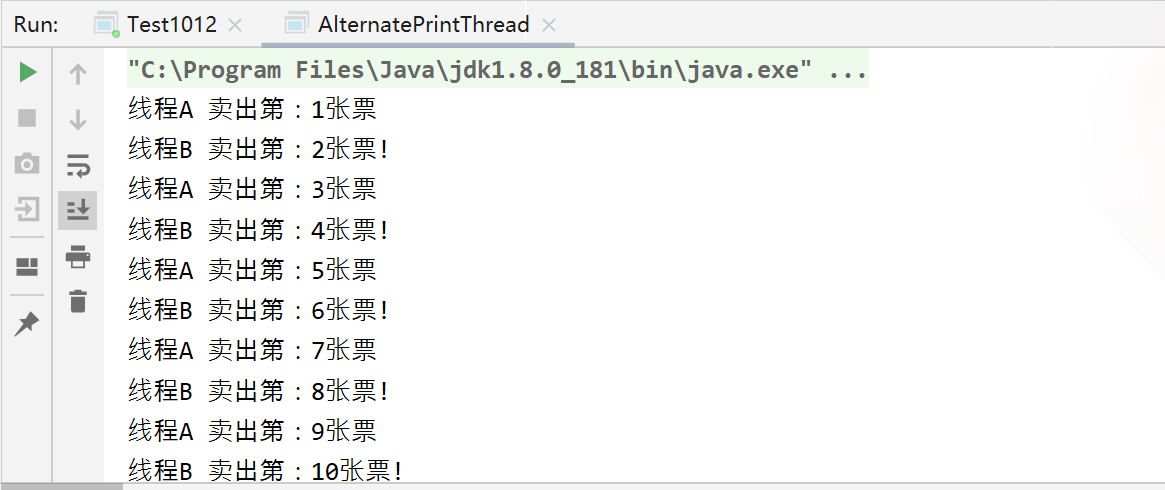
结果:

方法二(Volatile)
解题思路
定义一个volatile修饰的共享变量flag,当flag为false时,t2线程让出系统资源,自己进入就绪状态,让t1先执行,t1获取资源后,首先跳过while判断,打印奇数,修改flag为true,下次循环时,就会让出资源,此时t2从就绪状态进入执行状态,跳过while判断,打印偶数,修改flag为false,下次循环时,就会让出资源。如此不断交替执行,直到打印完所有奇数偶数张票。
代码实现:
1 //方法二(Volatile) 2 public void test2(){ 3 Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> { 4 for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i += 2) { 5 while (flag2) { 6 Thread.yield(); 7 } 8 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 卖出第 :" + i +" 张票!"); 9 flag2 = true; 10 } 11 12 }, "线程A"); 13 14 Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> { 15 for (int i = 2; i <= 100; i += 2) { 16 while (!flag2) { 17 Thread.yield(); 18 } 19 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 卖出第 :" + i +" 张票!"); 20 flag2 = false; 21 } 22 }, "线程B"); 23 t1.start(); 24 t2.start(); 25 }
结果:

方法三(Semaphore)
解题思路
定义两个信号量,一个许可为1,一个许可为0。首先许可为0的会阻塞,所以t1线程先执行,通过s1.acquire()消耗许可,打印奇数,此时s1许可为0,t1阻塞,同时s2.release()获得一个许可,t2线程通过s2.acquire()消耗许可,打印偶数,此时s2许可又变为0,t2阻塞,同时s1.release()获得一个许可。如此反复执行,直到打印完所有的数。
代码实现:
1 //方法三(Semaphore) 2 public void test3(){ 3 Semaphore s1 = new Semaphore(1); 4 Semaphore s2 = new Semaphore(0); 5 Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> { 6 for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i += 2) { 7 try { 8 s1.acquire(); //获取令牌 9 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 卖出第 :" + i +" 张票!"); 10 s2.release(); //释放令牌 11 } catch (Exception e) { 12 e.printStackTrace(); 13 } 14 15 } 16 }, "线程A"); 17 Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> { 18 for (int i = 2; i <= 100; i += 2) { 19 try { 20 s2.acquire(); 21 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 卖出第 :" + i +" 张票!"); 22 s1.release(); 23 } catch (Exception e) { 24 e.printStackTrace(); 25 } 26 } 27 }, "线程B"); 28 t1.start(); 29 t2.start(); 30 }
结果:

方法四(ReentrantLock + Condition)
解题思路
首先定义一个lock和一个condition。当flag为false时,t2会阻塞,此时t1先执行,打印奇数张票,通过condition唤醒t2,修改flag为true,下次循环自己就会进入阻塞状态。t2被唤醒后,由于flag已经变为true,跳过while判断,打印偶数张票,唤醒t1,修改flag,自己阻塞,如此反复。
代码实现:
1 //方法四(ReentrantLock) 2 public void test4(){ 3 Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> { 4 for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i += 2) { 5 lock.lock(); 6 while (flag3) { 7 try { 8 condition.await(); 9 Thread.sleep(200); 10 } catch (Exception e) { 11 e.printStackTrace(); 12 } 13 } 14 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 卖出第:" + i +"张票"); 15 condition.signal(); 16 flag3 = true; 17 lock.unlock(); 18 } 19 }, "窗口1"); 20 21 Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> { 22 for (int i = 2; i <= 100; i += 2) { 23 lock.lock(); 24 while (!flag3) { 25 try { 26 condition.await(); 27 Thread.sleep(200); 28 } catch (Exception e) { 29 e.printStackTrace(); 30 } 31 } 32 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 卖出第:" + i +"张票"); 33 condition.signal(); 34 flag3 = false; 35 lock.unlock(); 36 } 37 }, "窗口2"); 38 t1.start(); 39 t2.start(); 40 }
结果:

方法五(SynchronousQueue阻塞队列)
解题思路
定义一个阻塞队列,t2线程调用put或tranfer往队列里放数据时,会阻塞,所以t1先执行,取走之前放进来的奇数张票,并打印,然后将偶数put或tranfer到队列,t1阻塞,t2继续执行,如此反复执行。
代码实现:
1 //方法五(SynchronousQueue阻塞队列) 2 public void test5(){ 3 //定义奇偶数数组 4 int[] even = new int[50]; 5 int[] odd = new int[50]; 6 int a =0; 7 for(int i=0;i<100;i++){ 8 if(i%2==0){ 9 odd[a]=i+1; //偶数 2 4 6 8 10 10 a++; 11 }else{ 12 even[a-1]=i+1; //奇数 1 3 5 7 9 13 } 14 } 15 SynchronousQueue<Integer> queue=new SynchronousQueue<>(); 16 new Thread(()->{ 17 try{ 18 for(int i:even){ 19 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 卖出第:" + queue.take() +"张票"); 20 queue.put(i); 21 } 22 } 23 catch(Exception e){ 24 e.printStackTrace(); 25 } 26 },"线程A").start(); 27 new Thread(()->{ 28 try{ 29 for(int i:odd){ 30 queue.put(i); 31 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 卖出第:" + queue.take() +"张票"); 32 } 33 } 34 catch(Exception e){ 35 e.printStackTrace(); 36 } 37 },"线程B").start(); 38 }
SynchronousQueue是一个没有容量的队列,它的put操作和take操作之间是相互依赖的,即put操作必须在take操作准备好时才能将元素“推”过去,反之take操作也必须在put操作准备推元素的时候才能获取到元素。有人可能会说只有1个容量大小的BlockingQueue也能实现该操作,但是它们之间有着本质的不同
1、SynchronousQueue在put时,如果另一个线程没有执行take操作,put线程会一直阻塞;而BlockingQueue在put一个元素时,第一次是不会阻塞的,只有第二次因为容量满了put操作才阻塞,而SynchronousQueue在第一次就阻塞;
2、从第1点就可以看出SynchronousQueue容量为0,而BlockingQueue至少有容纳1个元素的空间。
结果:
至此:5中交替打印卖票的方法就总结完了!