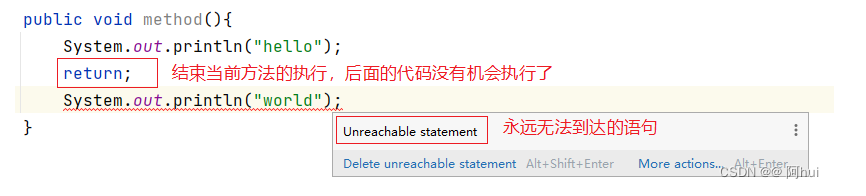
数组:内存空间连续,数据类型统一,下标从0开始
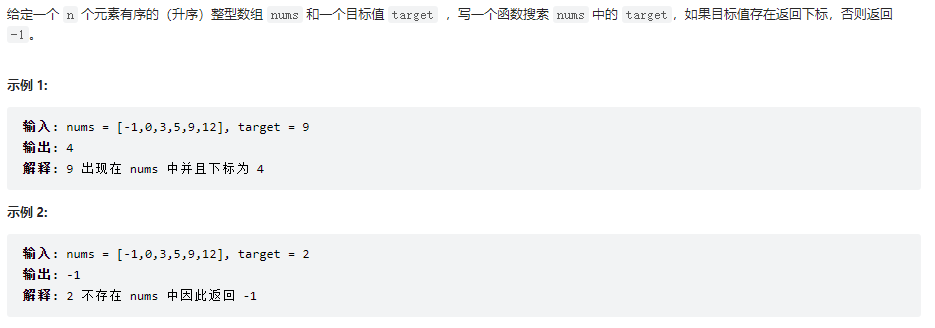
二分查找
class Solution {
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
// 方法一:暴力解法
// for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
// if(nums[i] == target){//找到目标值
// return i;
// }
// }
// return -1;
// 方法二:二分查找(元素有序且无重复元素),使用迭代,执行速度快,但是内存消耗大
// return binarySearch(nums, target, 0, nums.length-1);
// 方法三:二分查找,统一使用左闭右闭区间
// 上来先处理边界条件
if(target < nums[0] || target > nums[nums.length - 1]){
return -1;
}
int left = 0;
int right = nums.length - 1;//右闭区间
int mid = (left + right) >> 1;
while(left <= right){//因为取得数组区间左右都是闭的,所以取等号的时候也能满足条件,还不需要退出循环
if(target == nums[mid]){
return mid;
}else if(target < nums[mid]){
right = mid -1;//往左区间缩
}else{
left = mid +1;
}
mid = (left + right) >> 1;
}
return -1;
}
// public int binarySearch(int[] nums, int target, int start, int end){
// int mid = (start+end)/2;
// int find = -1;
// if(start > end){//没有找到
// return -1;
// }
// if(target == nums[mid]){
// return mid;
// }else if(target < nums[mid]){
// find = binarySearch(nums, target, start, mid-1);
// }else{
// find = binarySearch(nums, target, mid+1, end);
// }
// return find;
// }
}
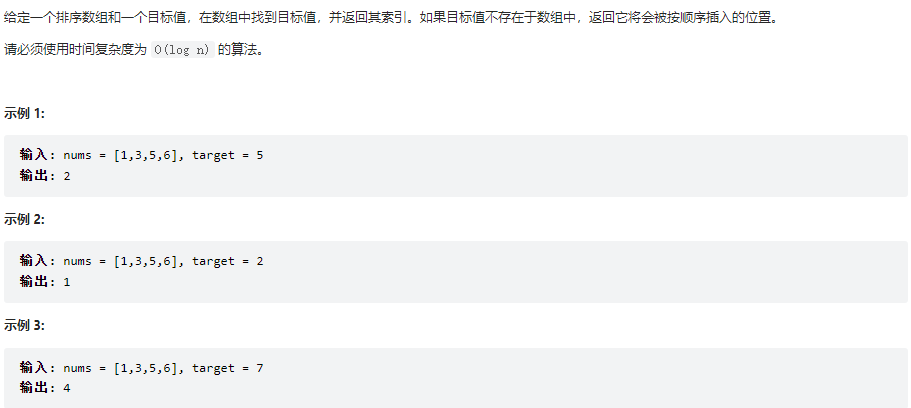
搜索插入位置
class Solution {
public int searchInsert(int[] nums, int target) {
// 有序数组,考虑用二分查找
int left = 0;
int right = nums.length - 1;
int mid = (left + right) >> 1;
if(target < nums[left]){
return left;
}
if(target > nums[right]){
return right + 1;
}
while(left <= right){
if(target == nums[mid]){
return mid;
}else if(target < nums[mid]){
right = mid -1;
}else{
left = mid + 1;
}
mid = (left + right) >> 1;
}
return left;//找不到,返回需要插入的位置
}
}
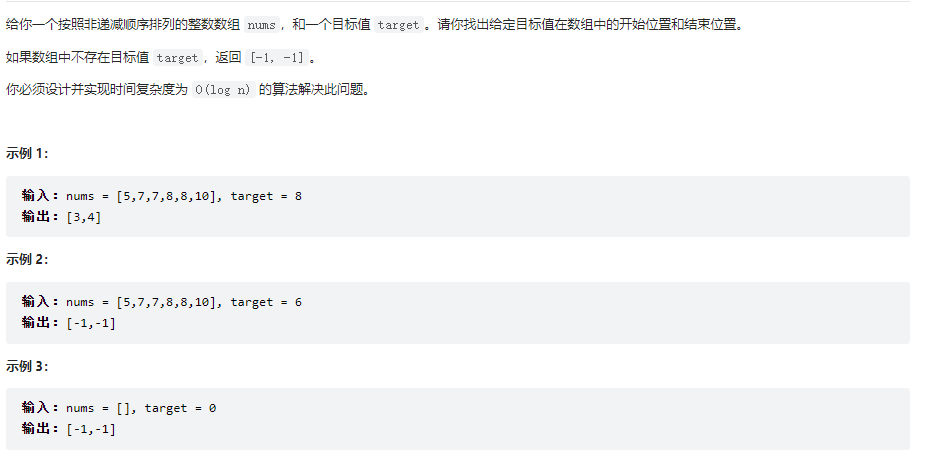
在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
class Solution {
public int[] searchRange(int[] nums, int target) {
// 非递减说明是升序的,但可以有重复元素
int[] arr = {-1, -1};
if(nums.length == 0){
return arr;
}
int left = 0;
int right = nums.length - 1;
int mid = (left + right) >> 1;
if(target < nums[left] || target > nums[right]){
return arr;//边界值
}
int leftPoint;//目标数组的开始位置
int rightPoint;//目标数组的结束位置
while(left <= right){
if(target == nums[mid]){
leftPoint = mid;
rightPoint = mid;
while(leftPoint >= 0 && target == nums[leftPoint]){
arr[0] = leftPoint;
leftPoint--;//向左寻找重复元素
}
while(rightPoint <= (nums.length - 1) && target == nums[rightPoint]){
arr[1] = rightPoint;
rightPoint++;//向右寻找重复元素
}
return arr;//返回找到的目标值的位置
}else if(target < nums[mid]){
right = mid - 1;
}else{
left = mid + 1;
}
mid = (left + right) >> 1;
}
return arr;//没有找到
}
}
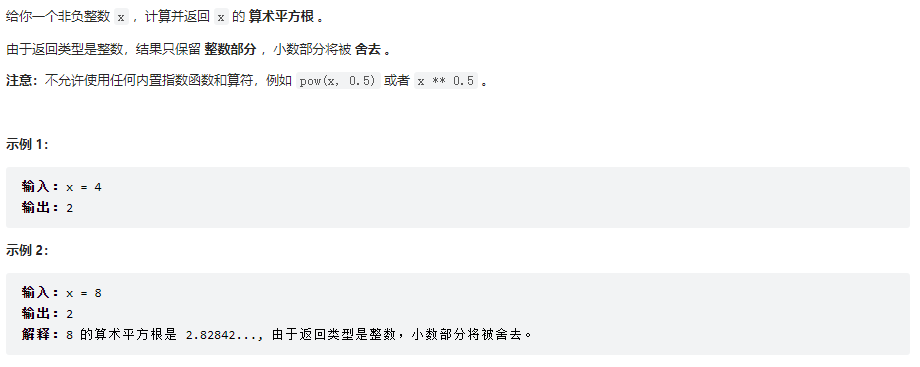
69、x的平方根
class Solution {
public int mySqrt(int x) {
// 使用二分查找
int left = 0;
int right = x;
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
while(left <= right){
if((long)mid * mid < x){
left = mid + 1;
}else if((long)mid * mid > x){
right = mid - 1;
}else{
return mid;
}
mid = (left + right) / 2;
}
return right;
}
}
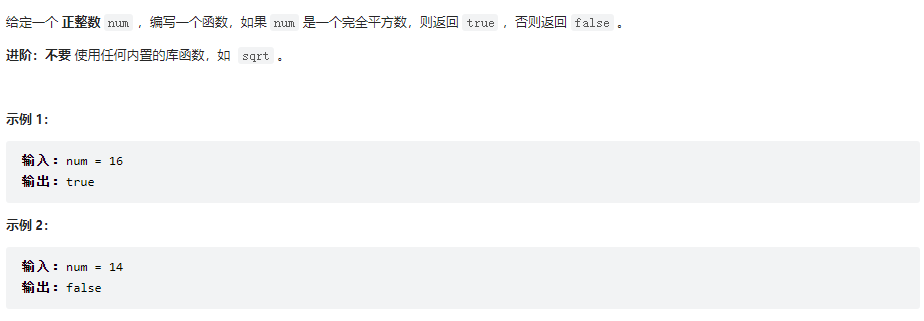
367、有效的完全平方数
class Solution {
public boolean isPerfectSquare(int num) {
int left = 0, right = num;
while(left <= right){
int mid = (left + right) >> 1;
if((long) mid * mid == num){
return true;
}else if((long) mid * mid < num){
left = mid + 1;
}else{
right = mid - 1;
}
}
return false;
}
}
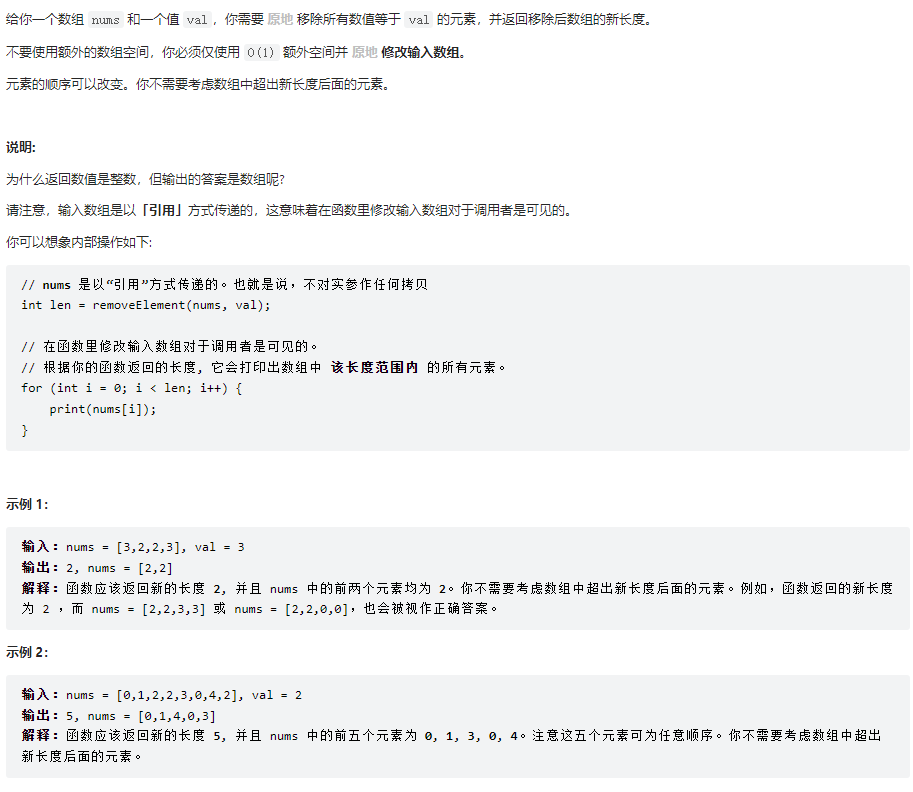
移除元素
class Solution {
public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
// 原地移除,所有元素
// 数组内元素可以乱序
// 方法一:暴力解法,不推荐,时间复杂度O(n^2)
// int right = nums.length;//目标数组长度,右指针
// for(int i = 0; i < right; i++){
// if(val == nums[i]){
// right--;//找到目标数值,目标数长度减一,右指针左移
// for(int j = i; j < right; j++){
// nums[j] = nums[j + 1];//数组整体左移一位(数组元素不能删除,只能覆盖)
// }
// i--;//左指针左移
// }
// }
// return right;
// 方法二:快慢指针,时间复杂度O(n)
// int solwPoint = 0;
// for(int fastPoint = 0; fastPoint < nums.length; fastPoint++){
// if(nums[fastPoint] != val){
// nums[solwPoint] = nums[fastPoint];
// solwPoint++;
// }
// }
// return solwPoint;
// 方法三:注意元素的顺序可以改变,使用相向指针,时间复杂度O(n)
int rightPoint = nums.length - 1;
int leftPoint = 0;
while(rightPoint >= 0 && nums[rightPoint] == val){
rightPoint--;
}
while(leftPoint <= rightPoint){
if(nums[leftPoint] == val){
nums[leftPoint] = nums[rightPoint--];
}
leftPoint++;
while(rightPoint >= 0 && nums[rightPoint] == val){
rightPoint--;
}
}
return leftPoint;
}
}
26、删除排序数组中的重复项
class Solution {
public int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) {
// 相对顺序一致,所以不能使用相向指针。
// 考虑使用快慢指针
if(nums.length == 1){
return 1;
}
int slowPoint = 0;
for(int fastPoint = 1; fastPoint < nums.length; fastPoint++){
if(nums[slowPoint] != nums[fastPoint]){
nums[++slowPoint] = nums[fastPoint];
}
}
return slowPoint + 1;
}
}
283、移动零
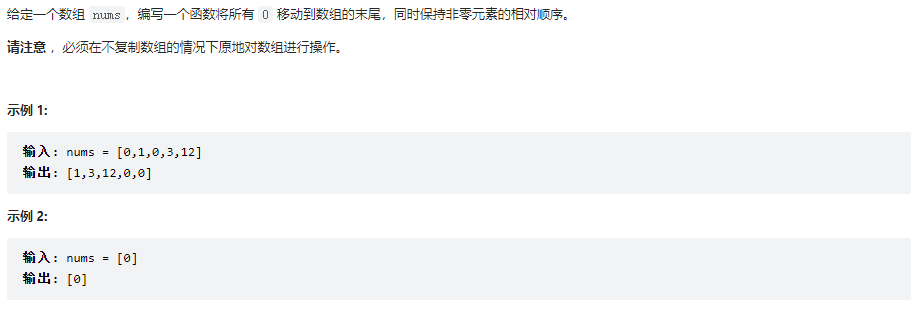
class Solution {
public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {
// 要保持相对顺序,不能用相向指针
int slowPoint = 0;
for(int fastPoint = 0; fastPoint < nums.length; fastPoint++){
if(nums[fastPoint] != 0){
nums[slowPoint++] = nums[fastPoint];//所有非零元素移到左边
}
}
for(; slowPoint < nums.length; slowPoint++){
nums[slowPoint] = 0;//把数组末尾置零
}
}
}
844、比较含退格的字符串
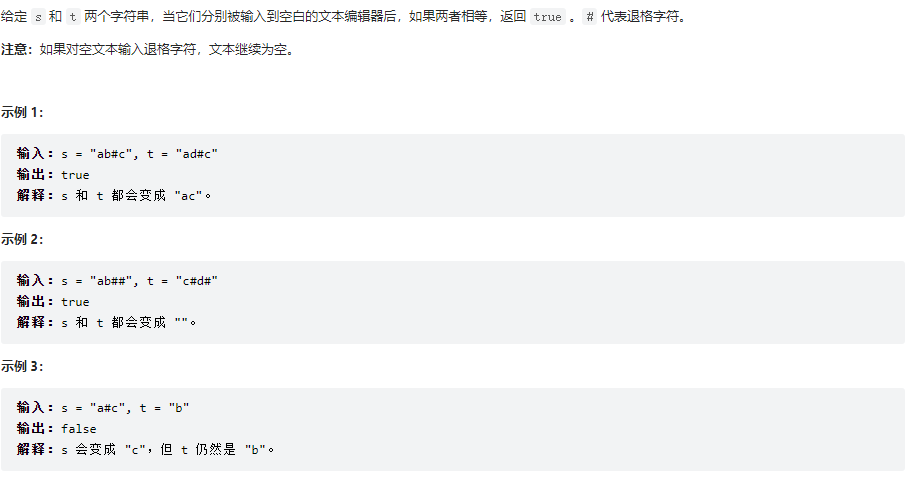
class Solution {
public boolean backspaceCompare(String s, String t) {
// 从前往后的话不确定下一位是不是"#",当前位需不需要消除,所以采用从后往前的方式
int countS = 0;//记录s中"#"的数量
int countT = 0;//记录t中"#"的数量
int rightS = s.length() - 1;
int rightT = t.length() - 1;
while(true){
while(rightS >= 0){
if(s.charAt(rightS) == '#'){
countS++;
}else{
if(countS > 0){
countS--;
}else{
break;
}
}
rightS--;
}
while(rightT >= 0){
if(t.charAt(rightT) == '#'){
countT++;
}else{
if(countT > 0){
countT--;
}else{
break;
}
}
rightT--;
}
if(rightT < 0 || rightS < 0){
break;
}
if(s.charAt(rightS) != t.charAt(rightT)){
return false;
}
rightS--;
rightT--;
}
if(rightS == -1 && rightT == -1){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
有序数组的平方
class Solution {
public int[] sortedSquares(int[] nums) {
// 用相向的双指针
int[] arr = new int[nums.length];
int index = arr.length - 1;
int leftPoint = 0;
int rightPoint = nums.length - 1;
while(leftPoint <= rightPoint){
if(Math.pow(nums[leftPoint], 2) > Math.pow(nums[rightPoint], 2)){
arr[index--] = (int)Math.pow(nums[leftPoint], 2);
leftPoint++;
}else{
arr[index--] = (int)Math.pow(nums[rightPoint], 2);
rightPoint--;
}
}
return arr;
}
}
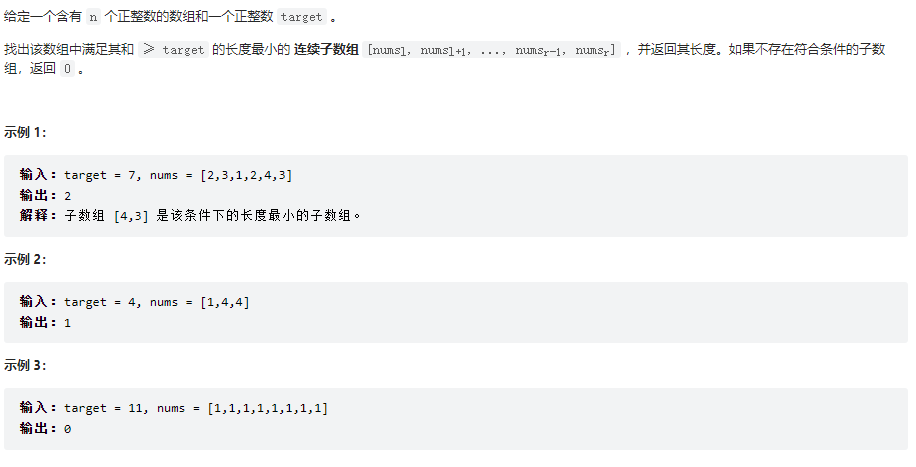
长度最小的子数组
class Solution {
public int minSubArrayLen(int target, int[] nums) {
// 注意是连续子数组
// 使用滑动窗口,实际上还是双指针
int left = 0;
int sum = 0;
int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(int right = 0; right < nums.length; right++){//for循环固定的是终止位置
sum += nums[right];
while(sum >= target){
result = Math.min(result, right - left + 1);//记录最小的子数组
sum -= nums[left++];
}
}
return result == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 0 : result;
}
}
904、水果成篮
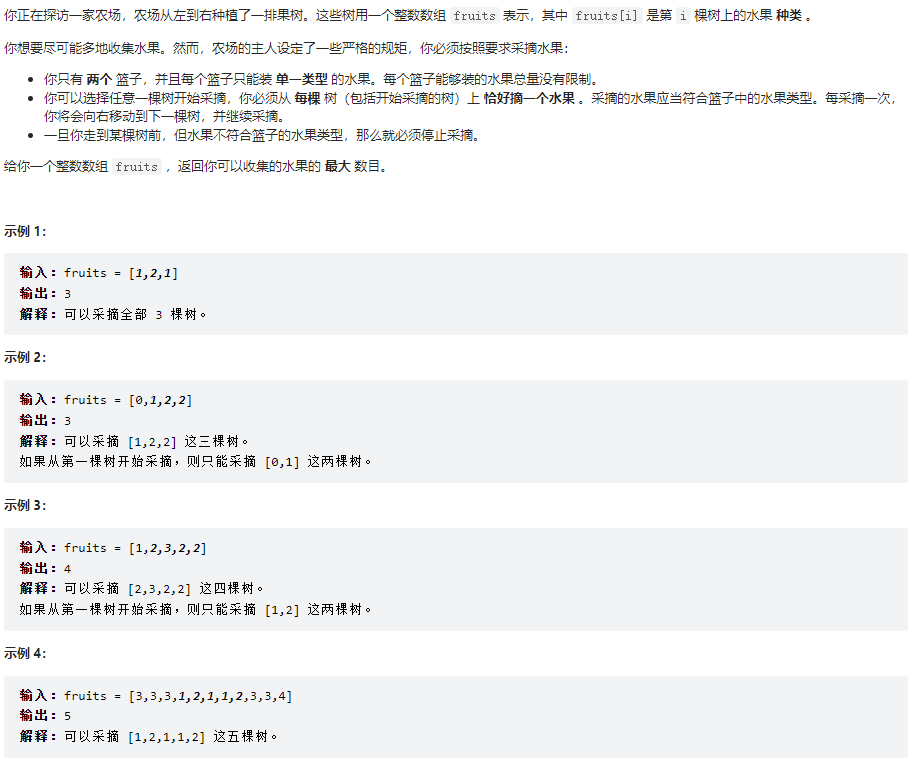
class Solution {
public int totalFruit(int[] fruits) {
// 此题也可以使用滑动窗口
int maxNumber = 0;
int left = 0;
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();//用哈希表记录被使用的篮子数量,以及每个篮子中的水果数量
for(int right = 0; right < fruits.length; right++){
map.put(fruits[right], map.getOrDefault(fruits[right], 0) + 1);//往篮子里面放水果
while(map.size() > 2){//放进去的水果不符合水果类型
map.put(fruits[left], map.get(fruits[left]) - 1);
if(map.get(fruits[left]) == 0){
map.remove(fruits[left]);
}
left++;
}
maxNumber = Math.max(maxNumber, right - left + 1);
}
return maxNumber;
}
}
螺旋矩阵 II
class Solution {
public int[][] generateMatrix(int n) {
// 方法一:直接按序输出
int[][] arr = new int[n][n];
int top = 0;
int buttom = n - 1;
int left = 0;
int right = n - 1;;
int index = 1;
while(left <= right && top <= buttom && index <= n*n){
for(int i = left; i <= right; i++){
arr[top][i] = index++;
}
top++;
for(int i = top; i <= buttom; i++){
arr[i][right] = index++;
}
right--;
for(int i = right; i >= left; i--){
arr[buttom][i] = index++;
}
buttom--;
for(int i = buttom; i >= top; i--){
arr[i][left] = index++;
}
left++;
}
return arr;
}
}
class Solution {
public List<Integer> spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
int top = 0;
int buttom = matrix.length - 1;
int left = 0;
int right = matrix[0].length - 1;
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
while(left <= right && top <= buttom){
for(int i = left; i <= right; i++){
if(top <= buttom)
list.add(matrix[top][i]);
}
top++;
for(int i = top; i <= buttom; i++){
if(left <= right)
list.add(matrix[i][right]);
}
right--;
for(int i = right; i >= left; i--){
if(top <= buttom)
list.add(matrix[buttom][i]);
}
buttom--;
for(int i = buttom; i >= top; i--){
if(left <= right)
list.add(matrix[i][left]);
}
left++;
}
return list;
}
}
29 、顺时针打印矩阵

class Solution {
public int[] spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
if(matrix.length == 0){
return new int[0];
}
int top = 0;
int buttom = matrix.length - 1;
int left = 0;
int right = matrix[0].length - 1;
int[] arr = new int[matrix.length*matrix[0].length];
int index = 0;
while(left <= right && top <= buttom){
for(int i = left; i <= right; i++){
if(top <= buttom)
arr[index++] = matrix[top][i];
}
top++;
for(int i = top; i <= buttom; i++){
if(left <= right)
arr[index++] = matrix[i][right];
}
right--;
for(int i = right; i >= left; i--){
if(top <= buttom)
arr[index++] = matrix[buttom][i];
}
buttom--;
for(int i = buttom; i >= top; i--){
if(left <= right)
arr[index++] = matrix[i][left];
}
left++;
}
return arr;
}
}
链表:插入快,查询慢,存储不连续
分为单链表,双链表和循环链表
在链表中使用虚拟头结点,可以减少增删改查中对头结点的特殊处理
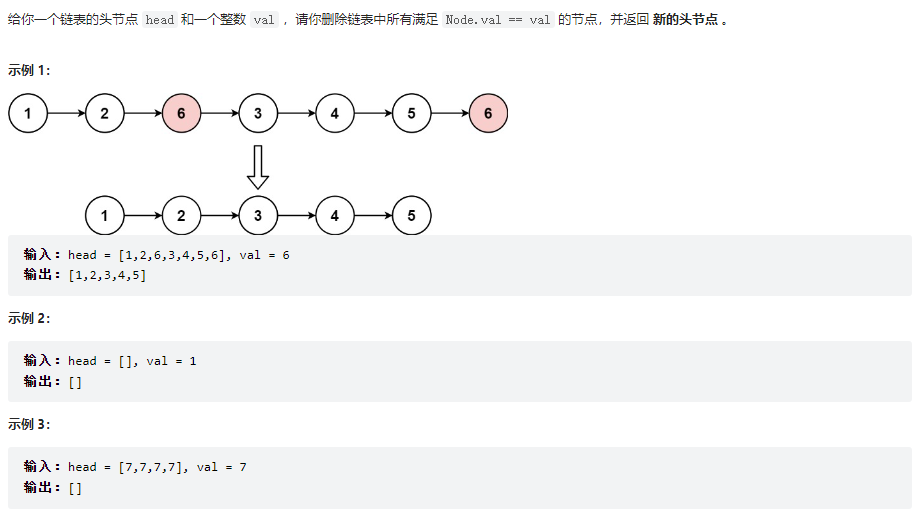
移除链表元素
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
// 方法一:设置虚节点方式,推荐方式
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1,head);
ListNode pre = dummy;
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.val == val){
pre.next = cur.next;
}else{
pre = cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return dummy.next;
// 方法二:时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(1)
if(head == null){//空链表的情况
return head;
}
while(head != null && head.val == val){//头结点为val的情况
head = head.next;
}
ListNode temp = head;
while(temp != null && temp.next != null){
while(temp != null && temp.next != null && temp.next.val == val){
if(temp.next.next != null){
temp.next = temp.next.next;
}else{//最后一个节点为val的情况
temp.next = null;
}
}
temp = temp.next;
}
return head;
}
}
707、设计链表

class MyLinkedList {
int size;
ListNode head;
ListNode tail;
// 初始化链表,构建虚拟的头结点和尾节点
public MyLinkedList() {
size = 0;
head = new ListNode(0);
tail = new ListNode(0);
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
public int get(int index) {
ListNode cur = head;
if(index > size - 1 || index < 0){
return -1;
}
while(index >= 0){
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
return cur.val;
}
public void addAtHead(int val) {
addAtIndex(0,val);
}
public void addAtTail(int val) {
addAtIndex(size,val);
}
public void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
if(index > size){
return;
}
if(index < 0 ){
index = 0;
}
size++;
ListNode temp = new ListNode(val);
ListNode cur = head;
while(index > 0){
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
temp.next = cur.next;
cur.next = temp;
temp.prev = cur;
}
public void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
ListNode cur = head;
if(index > size - 1 || index < 0){
return;
}
while(index > 0){
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
cur.next = cur.next.next;
size--;
}
}
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode prev;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
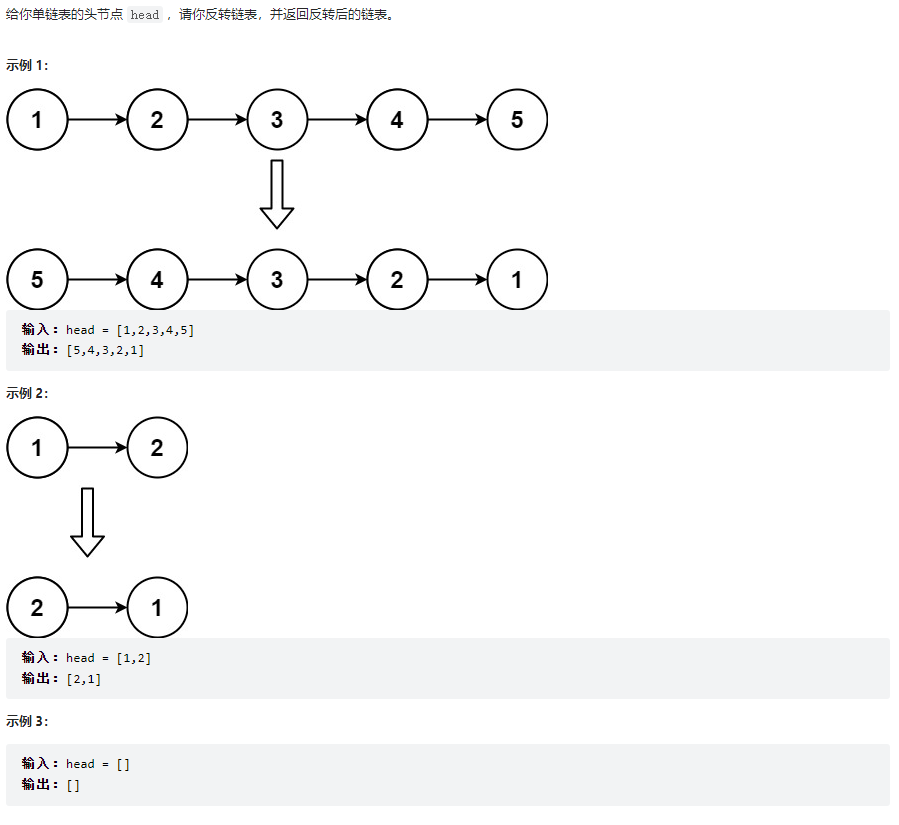
反转链表
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
// 方法一:在头结点不断插入
// if(head == null){
// return head;//空节点不需要反转
// }
// ListNode temp = head.next;//临时节点前移一位
// head.next = null;//代反转链表的头结点拆出来
// ListNode newHead = head;//待反转链表的头结点赋给新的链表
// while(temp != null){
// head = temp;//找出待反转链表的新头结点
// temp = temp.next;//临时节点前移一位
// head.next = null;//待反转链表的新头拆出来
// head.next = newHead;//待反转链表的心头指向新的链表
// newHead = head;//得到新的链表的新头
// }
// return newHead;
// 方法二:压栈,利用栈的先入后出
// if(head == null){
// return head;
// }
// Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack<>();
// ListNode temp = head;
// while(head != null){
// temp = head.next;
// head.next = null;
// stack.push(head);
// head = temp;
// }
// ListNode newHead = new ListNode();
// temp = newHead;
// while(!stack.isEmpty()){
// temp.next = stack.pop();
// temp = temp.next;
// }
// return newHead.next;
// 方法三:递归
return reverse(null, head);
// 方法四:从后往前递归
// if(head == null){
// return null;
// }
// if(head.next == null){
// return head;
// }
// ListNode newHead = reverseList(head.next);
// head.next.next = head;
// head.next = null;
// return newHead;
}
public ListNode reverse(ListNode pre, ListNode cur){
if(cur == null){
return pre;
}
ListNode temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
return reverse(cur,temp);
}
}
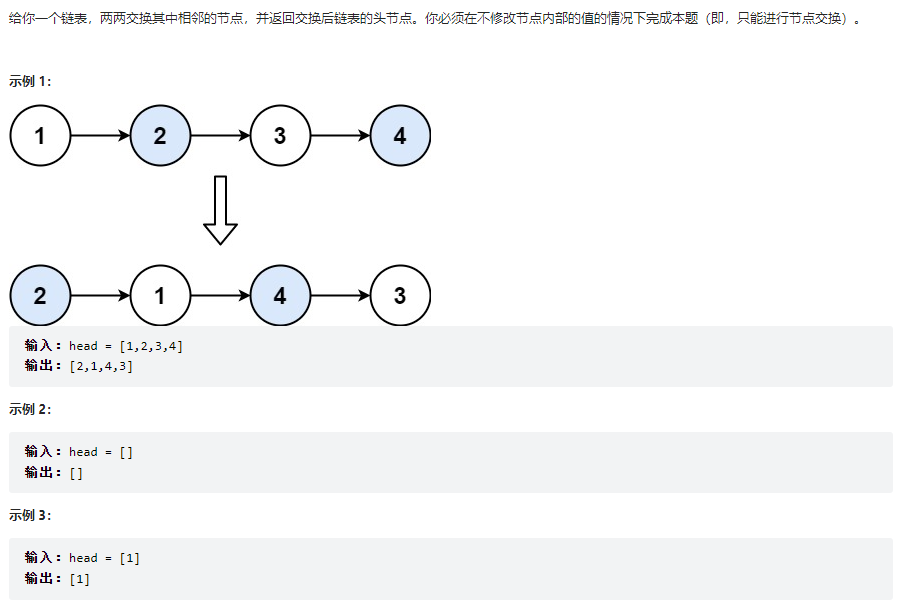
两两交换链表中的节点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
// 方法一:从前往后进行迭代
// if(head == null){
// return null;
// }
// if(head.next == null){
// return head;
// }
// ListNode temp = head.next;//依次记录偶数节点的位置
// head.next = head.next.next;//交换相邻的节点
// temp.next = head;
// temp.next.next = swapPairs(temp.next.next);//迭代交换下一个相邻的节点
// return temp;
// 方法二:双指针
if(head == null){
return null;
}
if(head.next == null){
return head;
}
ListNode temp = head.next;
ListNode pre = head.next;//记录新的头结点
while(temp != null){
head.next = head.next.next;//交换相邻的节点
temp.next = head;
if(head.next == null || head.next.next == null){
break;
}else{
head = head.next;//指向下一个相邻节点的奇数节点
temp.next.next = temp.next.next.next;//上一个相邻节点的偶数节点指向下一个节点的偶数节点
temp = head.next;//下一个相邻节点的偶数节点
}
}
return pre;
}
}
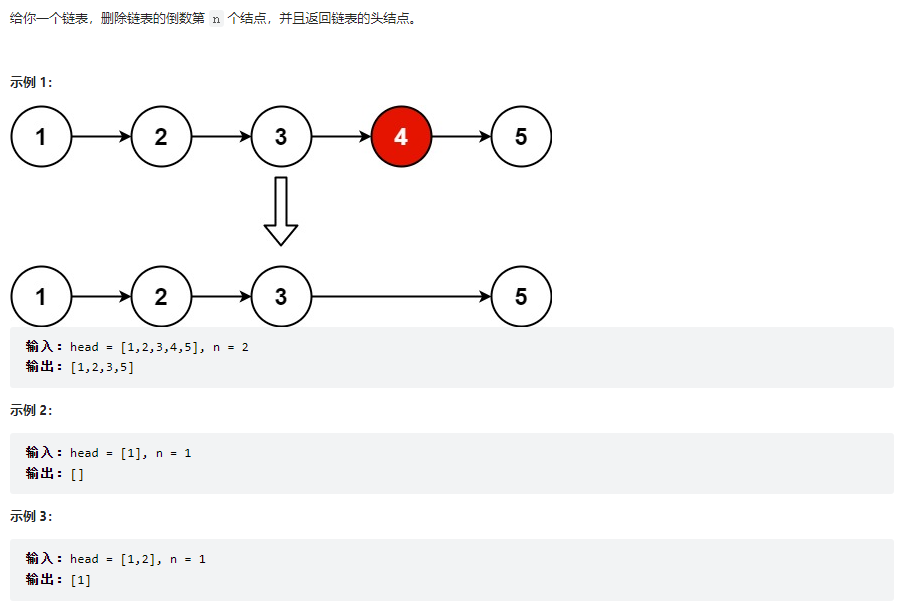
删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
// 方法一:快慢指针,返回头结点说明head的头结点不能动,所以把链表的地址赋给另外一个对象
// 添加虚拟头结点,方便操作。比如需要删除的是头结点的时候不需要单独考虑这种特殊情况
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode();
dummyHead.next = head;
ListNode cur = dummyHead;
ListNode temp = dummyHead;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
temp = temp.next;
}
while(temp.next != null){
cur = cur.next;
temp = temp.next;
}
cur.next = cur.next.next;
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
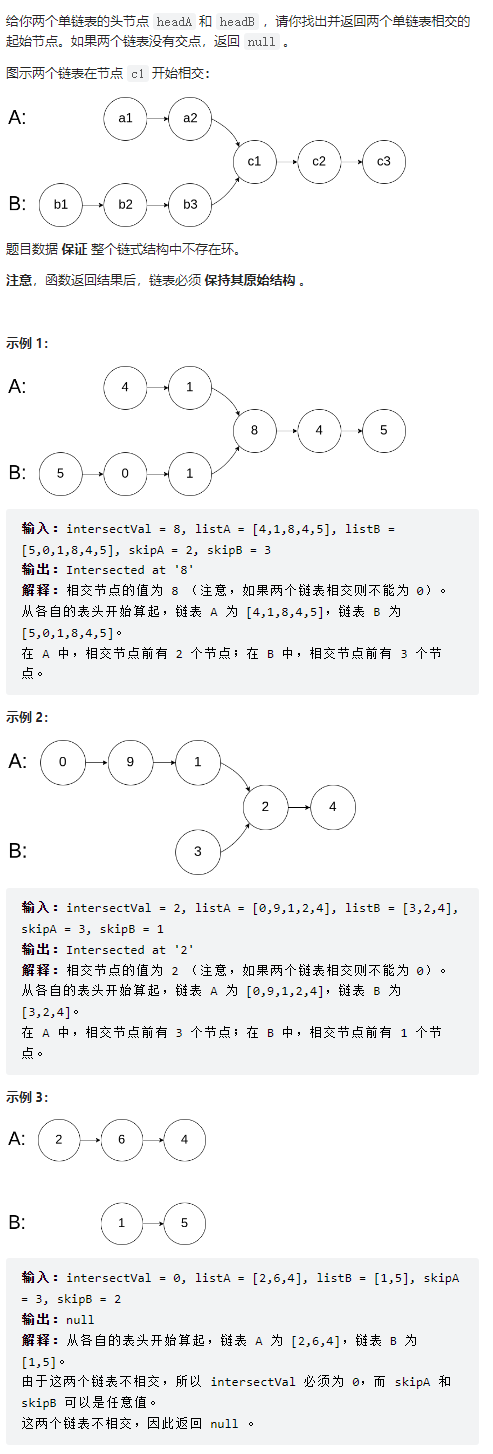
链表相交
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if(headA == null || headB == null){
return null;
}
ListNode dummyHeadA = headA;
int countA = 0;
int countB = 0;
ListNode dummyHeadB = headB;
while(dummyHeadA.next != null){
dummyHeadA = dummyHeadA.next;
countA++;
}
while(dummyHeadB.next != null){
dummyHeadB = dummyHeadB.next;
countB++;
}
if(dummyHeadA != dummyHeadB){
return null;//尾节点不相交则说明不相交
}
dummyHeadA = headA;
dummyHeadB = headB;
int index = (countA - countB) > 0 ? (countA - countB) : -(countA - countB);//两个链表的长度差
for(int i = 0; i < index; i++){//让较长的链表先移动index位
if((countA - countB) > 0){
dummyHeadA = dummyHeadA.next;
}else{
dummyHeadB = dummyHeadB.next;
}
}
while(dummyHeadA != dummyHeadB){//两个链表逐次向前移动,找出相交的第一个节点
dummyHeadA = dummyHeadA.next;
dummyHeadB = dummyHeadB.next;
}
return dummyHeadA;
}
}
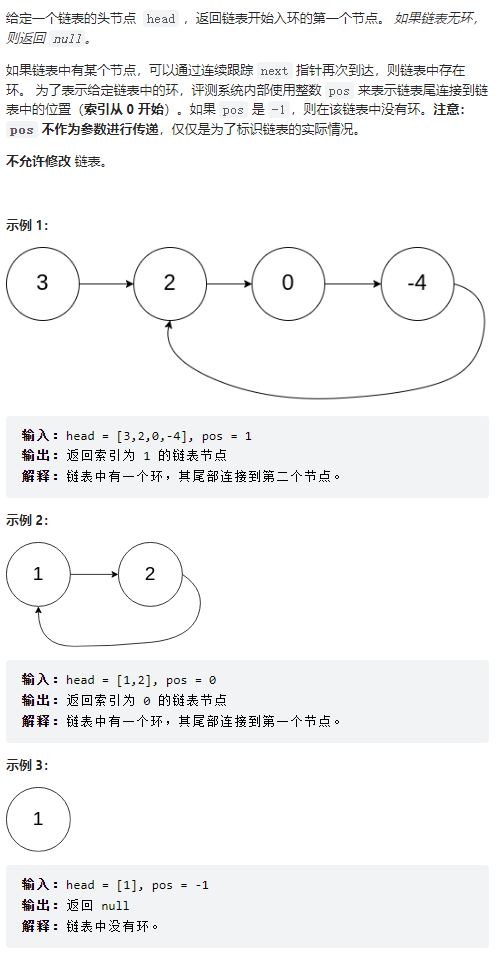
环形链表 II
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
int count = 0;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){//判断是否有环
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
count++;
if(fast == slow){
// 找环的入口
while(head != slow){
head = head.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return head;
}
}
return null;
}
}
哈希表:也叫散列表,用来快速判断一个元素是否出现在集合中,实际上是用空间换时间
有效的字母异位词
class Solution {
public boolean isAnagram(String s, String t) {
// 方法一:使用hashmap
// if(s.length() != t.length()){
// return false;
// }
// HashMap<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
// for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
// map.put(s.charAt(i), (map.getOrDefault(s.charAt(i), 0) + 1));
// }
// for(int i = 0; i < t.length(); i++){
// if(map.containsKey(t.charAt(i))){
// if(map.get(t.charAt(i)) == 1){
// map.remove(t.charAt(i));
// }else{
// map.put(t.charAt(i), (map.get(t.charAt(i)) - 1));
// }
// }else{
// return false;
// }
// }
// return true;
// 方法二:用数组来构造哈希表,字典解法
if(s.length() != t.length()){
return false;
}
int[] arr = new int[26];
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
int index = s.charAt(i) - 'a';
arr[index] = arr[index] + 1;
}
for(int i = 0; i < t.length(); i++){
int index = t.charAt(i) - 'a';
if(arr[index] != 0){
arr[index] = arr[index] - 1;
}else{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
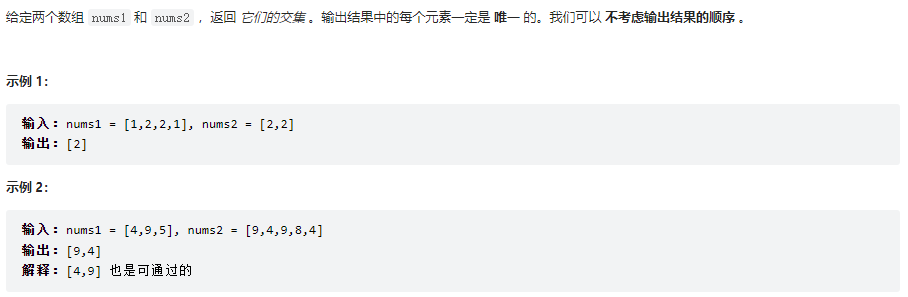
两个数组的交集
class Solution {
public int[] intersection(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
// 使用hashset,无序,且不能存储重复数据,符合题目要求
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
HashSet<Integer> record = new HashSet<>();
for(int i = 0; i < nums1.length; i++){
set.add(nums1[i]);
}
for(int i = 0; i < nums2.length; i++){
if(set.remove(nums2[i])){
record.add(nums2[i]);
}
}
return record.stream().mapToInt(x -> x).toArray();
}
}
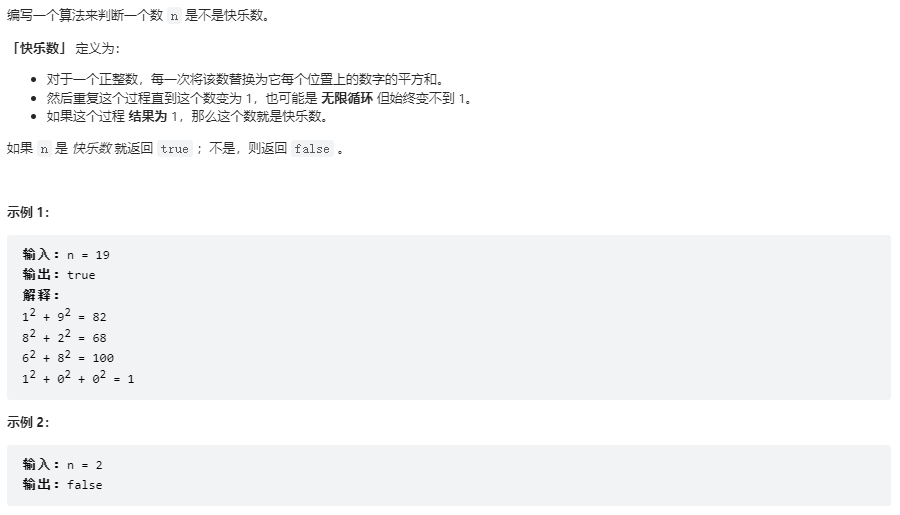
快乐数
class Solution {
public boolean isHappy(int n) {
// 使用hashset,当有重复的数字出现时,说明开始重复,这个数不是快乐数
HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet();
int sum = 0;
while(true){
while(n != 0){
sum = sum + (n%10)*(n%10);
n = n / 10;
}
if(sum == 1){
return true;
}
if(!set.add(sum)){
return false;
}
n = sum;
sum = 0;
}
}
}
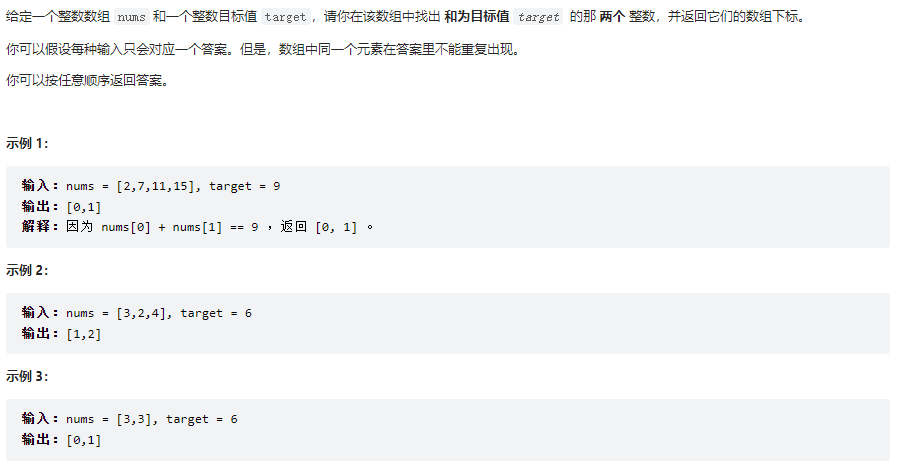
两数之和
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
// 方法一:暴力解法
// int[] arr = new int[2];
// for(int i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; i++){
// for(int j = i + 1 ; j < nums.length; j++){
// if(target == (nums[i] + nums[j])){
// return new int[]{i,j};
// }
// }
// }
// return new int[0];
// 方法二:HashMap
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
int find = target - nums[i];
if(map.containsKey(find)){
return new int[]{i, map.get(find)};
}else{
map.put(nums[i],i);
}
}
return null;
}
}
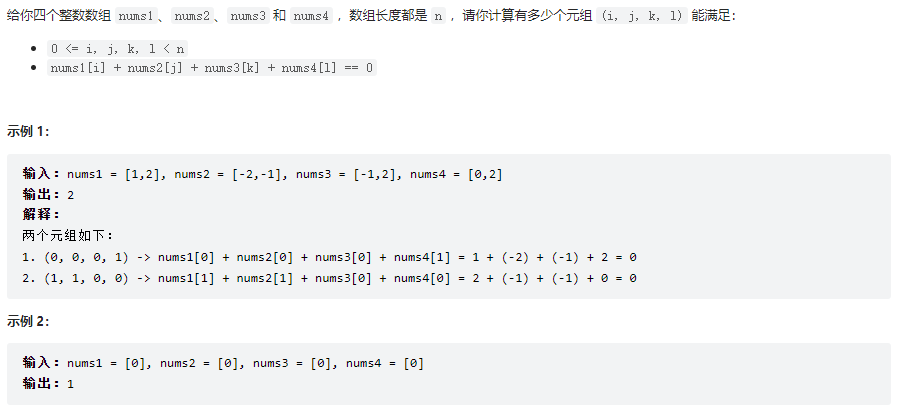
四数相加 II
class Solution {
public int fourSumCount(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int[] nums3, int[] nums4) {
// 四个数,用哈希表,参考代码随想录
HashMap<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int count = 0;
for(int i : nums1){
for(int j : nums2){
int temp = i + j;
if(map.containsKey(temp)){
map.put(temp, map.get(temp) + 1);
}else{
map.put(temp, 1);
}
}
}
for(int i : nums3){
for(int j : nums4){
int temp = 0- (i + j);
if(map.containsKey(temp)){
count += map.get(temp);
}
}
}
return count;
}
}
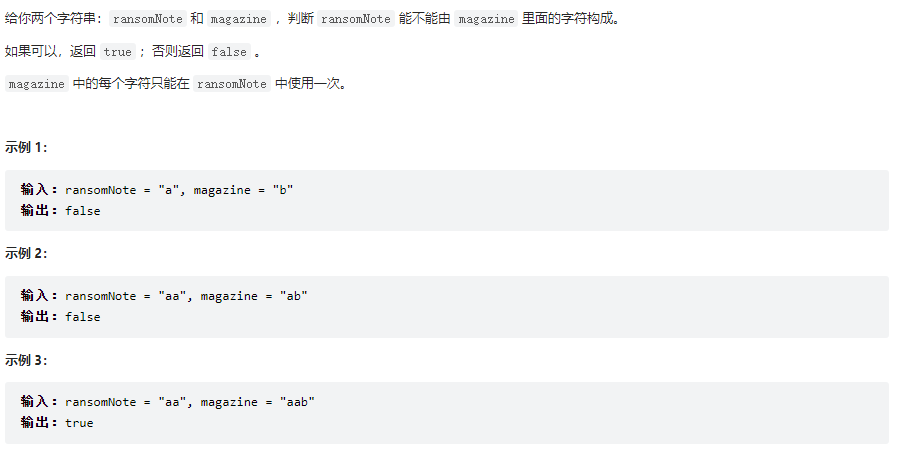
赎金信
class Solution {
public boolean canConstruct(String ransomNote, String magazine) {
// 方法一;hashmap
// HashMap<Character,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
// char temp;
// for(int i = 0; i < ransomNote.length(); i++){
// temp = ransomNote.charAt(i);
// if(map.containsKey(temp)){
// map.put(temp, map.get(temp) + 1);
// }else{
// map.put(temp, 1);
// }
// }
// for(int i = 0; i < magazine.length(); i++){
// temp = magazine.charAt(i);
// if(map.containsKey(temp)){
// if(map.get(temp) == 1){
// map.remove(temp);
// }else{
// map.put(temp, map.get(temp) - 1);
// }
// }
// }
// if(map.isEmpty()){
// return true;
// }else{
// return false;
// }
// 方法二:数组在哈希法的应用,比起方法一更加节省空间,因为字符串只有小写的英文字母组成
int[] arr = new int[26];
int temp;
for(int i = 0; i < ransomNote.length(); i++){
temp = ransomNote.charAt(i) - 'a';
arr[temp] = arr[temp] + 1;
}
for(int i = 0; i < magazine.length(); i++){
temp = magazine.charAt(i) - 'a';
if(arr[temp] != 0){
arr[temp] = arr[temp] - 1;
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
if(arr[i] != 0){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
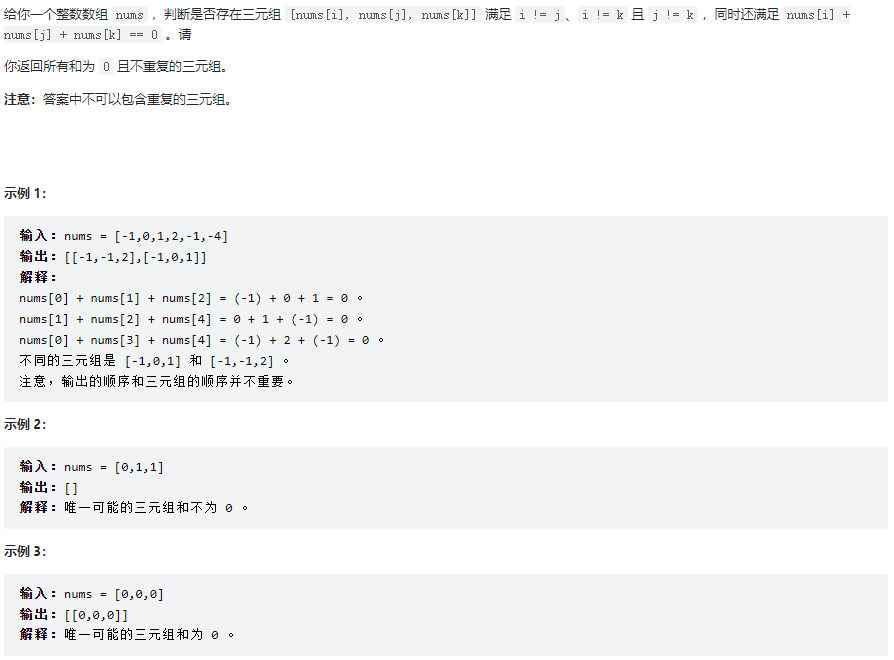
三数之和
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
// 如果考虑使用跟四数之和类似的求解方式,由于三元组是在同一个数组中寻找的,且要求不重复的三元组,因此求解会比较复杂
// 题目要求返回的是三元组的具体数值,而不是索引值,因此可以考虑使用双指针
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
Arrays.sort(nums);
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
if(nums[i] > 0){
return result;
}
if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]){
continue;
}
int left = i + 1;
int right = nums.length - 1;
while(left < right){
if((nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right]) > 0){
right--;
}else if((nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right]) < 0){
left++;
}else{
temp.add(nums[i]);
temp.add(nums[left]);
temp.add(nums[right]);
result.add(temp);
temp = new ArrayList<Integer>();
while(left < right && nums[right] == nums[right-1]){
right--;
}
while(left < right && nums[left] == nums[left+1]){
left++;
}
left++;
right--;
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
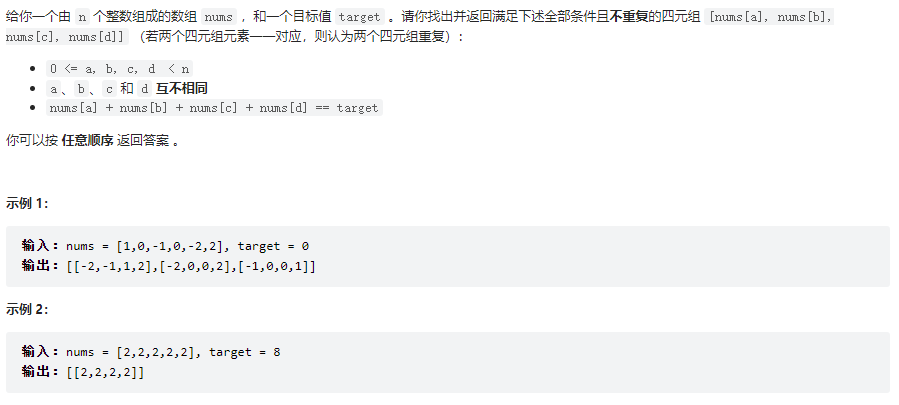
四数之和
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> fourSum(int[] nums, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
for(int i=0;i<nums.length-1;i++){
for(int j=0;j<nums.length-1-i;j++){
if(nums[j]>nums[j+1]){
int temp = nums[j+1];
nums[j+1] = nums[j];
nums[j] = temp;
}
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
if (nums[i] > 0 && nums[i] > target) {
return list;
}
if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]){
continue;
}
for(int j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++){
if(j > i + 1 && nums[j] == nums[j - 1]){
continue;
}
int left = j + 1;
int right = nums.length - 1;
while(left < right){
long sum = (long)(nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[left] + nums[right]);
if(sum > target){
right--;
}else if(sum < target){
left++;
}else{
list.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i] , nums[j] , nums[left] , nums[right]));
while(left < right && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]){
left++;
}
while(left < right && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]){
right--;
}
left++;
right--;
}
}
}
}
return list;
}
}
字符串:
反转字符串
class Solution {
public void reverseString(char[] s) {
// 左右指针
int leftNode = 0;
int rifhtNode = s.length - 1;
char temp;
while(leftNode <= rifhtNode){
temp = s[rifhtNode];
s[rifhtNode] = s[leftNode];
s[leftNode] = temp;
leftNode++;
rifhtNode--;
}
}
}
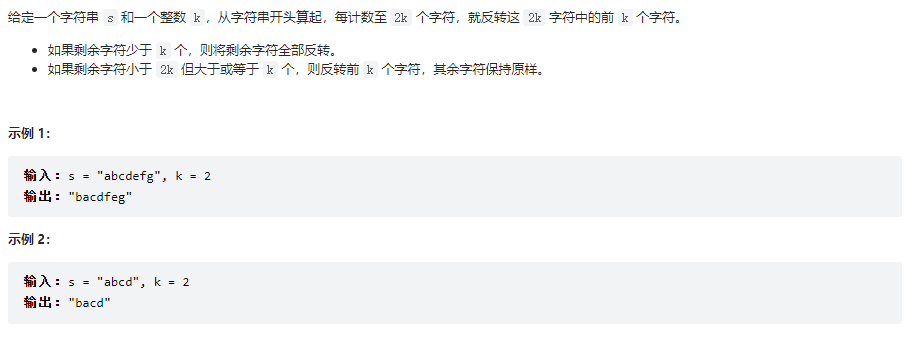
反转字符串 II
class Solution {
public String reverseStr(String s, int k) {
char[] arr = s.toCharArray();
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i=i+2*k){
if((i+k)<=arr.length){
reverse(arr,i,i+k-1);
}else{
reverse(arr,i,arr.length-1);
}
}
return new String(arr);
}
public void reverse(char[] arr, int left, int right){
while(left < right){
char temp = arr[left];
arr[left] = arr[right];
arr[right] = temp;
left++;
right--;
}
}
}
替换空格
class Solution {
public String replaceSpace(String s) {
StringBuffer target = new StringBuffer();
char temp;
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
temp = s.charAt(i);
if(temp == ' '){
target.append("%20");
}else{
target.append(temp);
}
}
return new String(target);
}
}
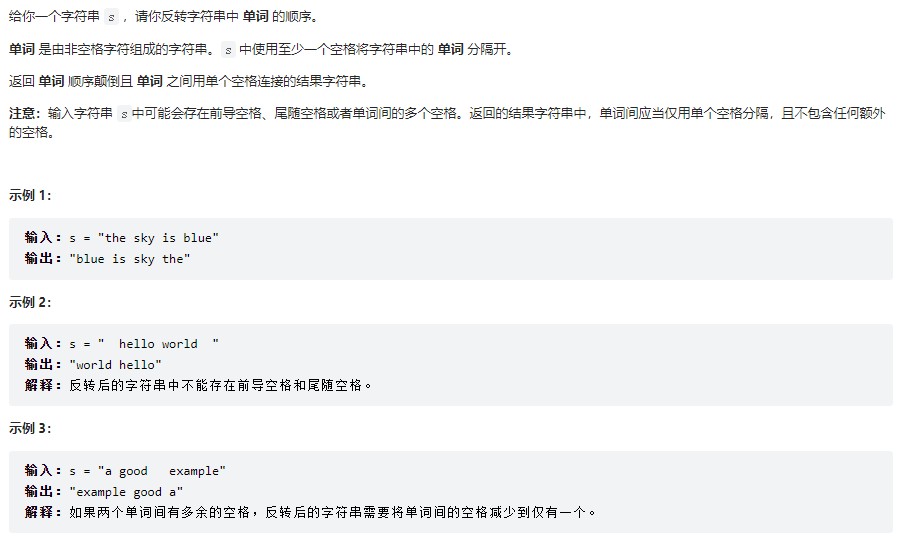
反转字符串中的单词
class Solution {
public String reverseWords(String s) {
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer();
int index = 0;
while(s.charAt(index)==' '){
index++;
}
for(;index < s.length();index++){
if(s.charAt(index)!=' '){
buffer.append(s.charAt(index));
}else{
while(index < s.length() && s.charAt(index)==' '){
index++;
}
if(index < s.length()){
buffer.append(' ');
buffer.append(s.charAt(index));
}
}
}
String arr = new String(buffer);
String[] result = arr.split(" ");
int left = 0;
int right = result.length - 1;
while(left < right){
String temp = result[left];
result[left] = result[right];
result[right] = temp;
left++;
right--;
}
StringBuffer buffer1 = new StringBuffer();
for(int a = 0; a < result.length; a++){
buffer1.append(result[a]);
if(a < result.length - 1){
buffer1.append(" ");
}
}
return new String(buffer1);
}
}
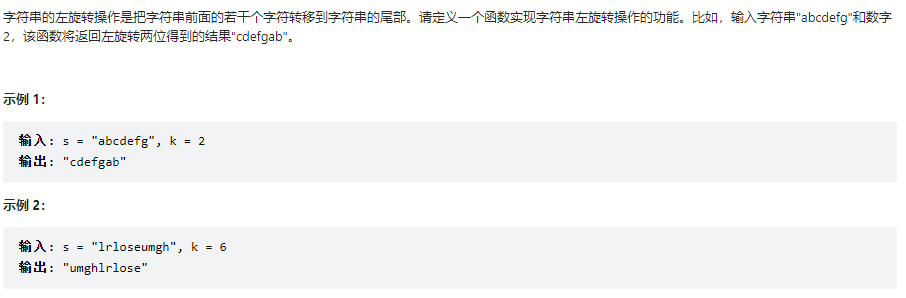
左旋转字符串
class Solution {
public String reverseLeftWords(String s, int n) {
// 先整体反转,在根据k进行部分反转
char[] str = s.toCharArray();
reverse(str, 0, str.length - 1);
reverse(str, 0, str.length - 1 - n);
reverse(str, str.length - n, str.length - 1);
return new String(str);
}
public void reverse(char[] str, int start, int end){
while(start < end){
str[start] ^= str[end];
str[end] ^= str[start];
str[start] ^= str[end];
start++;
end--;
}
}
}
找出字符串中第一个匹配项的下标
KMP字符串匹配:在主串中寻找子串的过程,称为模式匹配
KMP的主要思想是当出现字符串不匹配时,可以知道一部分之前已经匹配的文本内容,可以利用这些信息避免从头再去做匹配了。
前缀表:记录下标i之前(包括i)的字符串中,有多大长度的相同前缀后缀。
28

class Solution {
public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) {
int[] arr = kmp(needle);
for(int i = 0, j = 0; i < haystack.length(); i++){
while(j > 0 && haystack.charAt(i) != needle.charAt(j)){
j = arr[j - 1];
}
if(haystack.charAt(i) == needle.charAt(j)){
j++;
}
if(j == needle.length()){
return i - j + 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
public int[] kmp(String needle){
int[] next = new int[needle.length()];
for(int i = 1, j = 0; i < next.length; i++){
while(j > 0 && needle.charAt(i) != needle.charAt(j)){
j = next[j - 1];
}
if(needle.charAt(i) == needle.charAt(j)){
j++;
}
next[i] = j;
}
return next;
}
}
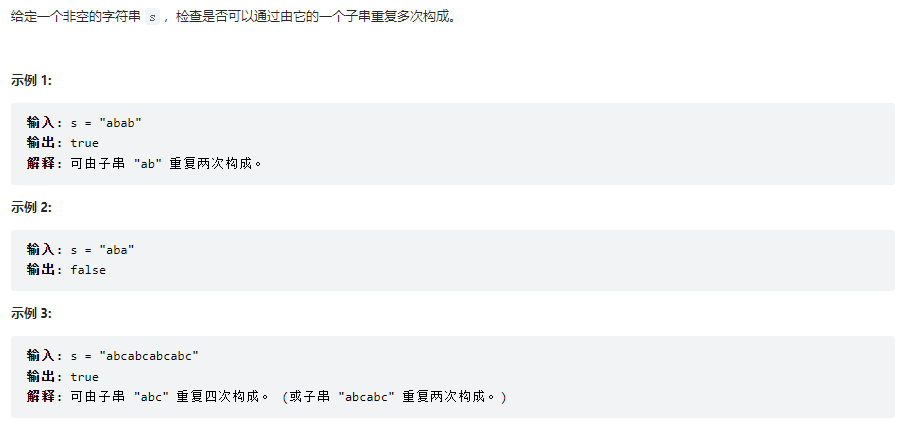
重复的子字符串
class Solution {
public boolean repeatedSubstringPattern(String s) {
int[] next = new int[s.length()];
next[0] = 0;
for(int i = 1, j = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
while(j > 0 && s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(j)){
j = next[j - 1];
}
if(s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j)){
j++;
}
next[i] = j;
}
if(next[next.length - 1] != 0 && next.length%(next.length - next[next.length - 1]) == 0){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
栈和队列:容器适配器,不提供迭代器
232、用栈实现队列

class MyQueue {
Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<>();
Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<>();
public MyQueue() {
}
public void push(int x) {
stack1.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
if(stack2.isEmpty()){
while(!stack1.isEmpty()){
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if(stack2.isEmpty()){
while(!stack1.isEmpty()){
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
if(stack1.isEmpty() && stack2.isEmpty()){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue obj = new MyQueue();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.peek();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
225、用队列实现栈

class MyStack {
Queue<Integer> queue1;
Queue<Integer> queue2;//用来备份栈的数据(除栈顶)
public MyStack() {
queue1 = new LinkedList<>();
queue2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
// 方法一:较为繁琐
// public void push(int x) {
// while(queue1.size() > 0){
// queue2.offer(queue1.poll());
// }
// while(queue2.size() > 0){
// queue1.offer(queue2.poll());
// }
// queue1.offer(x);
// }
// public int pop() {
// while(queue1.size() > 1){
// queue2.offer(queue1.poll());
// }
// int temp = queue1.poll();
// while(queue2.size() > 0){
// queue1.offer(queue2.poll());
// }
// return temp;
// }
// public int top() {
// while(queue1.size() > 1){
// queue2.offer(queue1.poll());
// }
// int temp = queue1.peek();
// while(queue1.size() > 0){
// queue2.offer(queue1.poll());
// }
// while(queue2.size() > 0){
// queue1.offer(queue2.poll());
// }
// return temp;
// }
// public boolean empty() {
// return queue1.isEmpty() && queue2.isEmpty();
// }
// 方法二:参考代码随想录
// public void push(int x) {
// queue2.offer(x);
// while(!queue1.isEmpty()){
// queue2.offer(queue1.poll());
// }
// Queue<Integer> temp = new LinkedList<>();
// queue1 = queue2;
// queue2 = temp;
// }
// public int pop() {
// return queue1.poll();
// }
// public int top() {
// return queue1.peek();
// }
// public boolean empty() {
// return queue1.isEmpty() && queue2.isEmpty();
// }
// 方法三:用单队列实现
public void push(int x) {
if(queue1.isEmpty()){
queue1.offer(x);
}else{
int count = queue1.size();
queue1.offer(x);
while(count > 0){
queue1.offer(queue1.poll());
count--;
}
}
}
public int pop() {
return queue1.poll();
}
public int top() {
return queue1.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return queue1.isEmpty();
}
}
/**
* Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack obj = new MyStack();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.top();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
20、有效的括号

class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
// 方法一:用字符串
// String s1 = "";
// if(s.length()%2 == 1){
// return false;
// }
// for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
// if(s.charAt(i) == '(' || s.charAt(i) == '[' || s.charAt(i) == '{'){
// s1 = s1 + s.charAt(i);
// }else if(s1.length() == 0){
// return false;
// }else if((s.charAt(i) == ']') && (s1.charAt(s1.length()-1) == '[')){
// s1 = s1.substring(0,s1.length() - 1);
// }else if((s.charAt(i) == '}') && (s1.charAt(s1.length()-1) == '{')){
// s1 = s1.substring(0,s1.length() - 1);
// }else if((s.charAt(i) == ')') && (s1.charAt(s1.length()-1) == '(')){
// s1 = s1.substring(0,s1.length() - 1);
// }else{
// return false;
// }
// }
// if(s1.length() == 0){
// return true;
// }else{
// return false;
// }
// 方法二:用栈
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
char[] arr = s.toCharArray();
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
if(arr[i] == '(' || arr[i] == '[' || arr[i] == '{'){
stack.push(arr[i]);
}else if(arr[i] == ')'){
if(stack.isEmpty() || stack.pop() != '('){
return false;
}
}else if(arr[i] == ']'){
if(stack.isEmpty() ||stack.pop() != '['){
return false;
}
}else if(arr[i] == '}'){
if(stack.isEmpty() ||stack.pop() != '{'){
return false;
}
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
1047、删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项
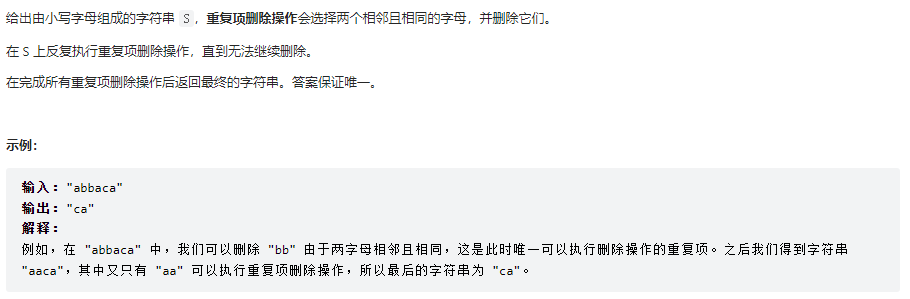
class Solution {
public String removeDuplicates(String s) {
// 方法一:用栈
char[] arr = s.toCharArray();
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
if(stack.isEmpty()){
stack.push(arr[i]);
}else if(stack.peek() == arr[i]){
stack.pop();
}else{
stack.push(arr[i]);
}
}
String str = "";
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
str = stack.pop() + str;
}
return str;
// // 方法二:双线队列
// char[] arr = s.toCharArray();
// ArrayDeque<Character> arraydeque = new ArrayDeque<>();
// for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
// if(arraydeque.isEmpty()){
// arraydeque.push(arr[i]);
// }else if(arraydeque.peek() == arr[i]){
// arraydeque.pop();
// }else{
// arraydeque.push(arr[i]);
// }
// }
// String str = "";
// while(!arraydeque.isEmpty()){
// str = arraydeque.pop() + str;
// }
// return str;
}
}
150、逆波兰表达式求值

class Solution {
public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
for(int i = 0; i < tokens.length; i++){
if(tokens[i].equals("+")){
stack.push(stack.pop() + stack.pop());
}else if(tokens[i].equals("-")){
stack.push(-stack.pop() + stack.pop());
}else if(tokens[i].equals("*")){
stack.push(stack.pop() * stack.pop());
}else if(tokens[i].equals("/")){
int divisor = stack.pop();
int dividend = stack.pop();
int temp = dividend/divisor;
stack.push(temp);
}else{
stack.push(Integer.valueOf(tokens[i]));
}
}
return stack.pop();
}
}
239、滑动窗口最大值
单调队列

class Solution {
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
Deque<Integer> deque = new LinkedList<>();//单调双向队列
int[] result = new int[nums.length - k + 1];
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
while(deque.peekFirst() != null && deque.peekFirst() < i - k + 1){
deque.pollFirst();
}
while(deque.peekLast() != null && nums[i] > nums[deque.peekLast()]){
deque.pollLast();
}
deque.offerLast(i);
if(i - k + 1 >= 0 ){
result[i - k + 1] = nums[deque.peekFirst()];
}
}
return result;
}
}
347、前 K 个高频元素
优先级队列,大顶堆,小顶堆

class Solution {
public int[] topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i: nums){
map.put(i, map.getOrDefault(i, 0) + 1);
}
PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<int[]>(){
public int compare(int[] m, int[] n){
return m[1] - n[1];
}
});
for(Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry: map.entrySet()){
if(pq.size() < k){
pq.add(new int[]{entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()});
}else{
if(pq.peek()[1] < entry.getValue()){
pq.poll();
pq.add(new int[]{entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()});
}
}
}
int[] arr = new int[k];
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
arr[i] = pq.poll()[0];
}
return arr;
}
}