1、使用 Array.prototype.some() 方法代替
some() 方法会在找到第一个符合条件的元素时停止循环。
例如:
let array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
array.some(function(element, index, array) {
if (element === 3) {
console.log("Found 3 at index " + index);
return true;
}
});上述代码会在找到第一个符合条件的元素(即 3)时停止循环。
2、使用 for循环代替
let array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
for(let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
if (array[i] === 3) {
console.log("Found 3 at index " + i);
break;
}
}上述代码也会在找到第一个符合条件的元素(即 3)时停止循环。
3、使用 try-catch 结构
可以在 forEach 循环内部使用 throw 语句来中断循环,并在外部使用 catch 语句来捕获该异常。
例如:
let array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
try {
array.forEach(function(element, index, array) {
if (element === 3) {
console.log("Found 3 at index " + index);
throw "StopIteration";
}
});
} catch (e) {
if (e !== "StopIteration") throw e;
}上述代码会在找到第一个符合条件的元素(即 3)时停止循环。
请注意,使用 throw 语句中断 forEach 循环可能会使代码变得更加复杂,并且容易出现错误。因此,如果可能的话,应该使用前面提到的 Array.prototype.some() 或 for 循环来代替。
4、使用自定义的迭代器函数
let array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
function forEach(array, callback) {
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
callback(array[i], i, array);
if (array[i] === 3) {
console.log("Found 3 at index " + i);
break;
}
}
}
forEach(array, function(element, index, array) {
console.log(element);
});上述代码会在找到第一个符合条件的元素(即 3)时停止循环。
这种方法虽然不够简洁,但是它可以在不改变原来的forEach函数的情况下,增加新的功能。
5、使用 Array.prototype.find() 或 Array.prototype.findIndex() 方法
find() 方法会在找到符合条件的第一个元素后返回该元素,并停止循环。
例如:
let array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
let found = array.find(function(element) {
return element === 3;
});
console.log(found);上述代码会在找到第一个符合条件的元素(即 3)时停止循环并返回该元素。
Array.prototype.findIndex() 方法可以返回第一个符合条件元素的索引。
使用 Array.prototype.find() 或 Array.prototype.findIndex() 方法可以在 forEach 循环中找到符合条件的第一个元素并停止循环。这两种方法是在找到符合条件的元素后返回该元素或索引,而不是像 some() 方法或 for 循环中需要再次返回一个布尔值或使用 throw 语句来中断循环。






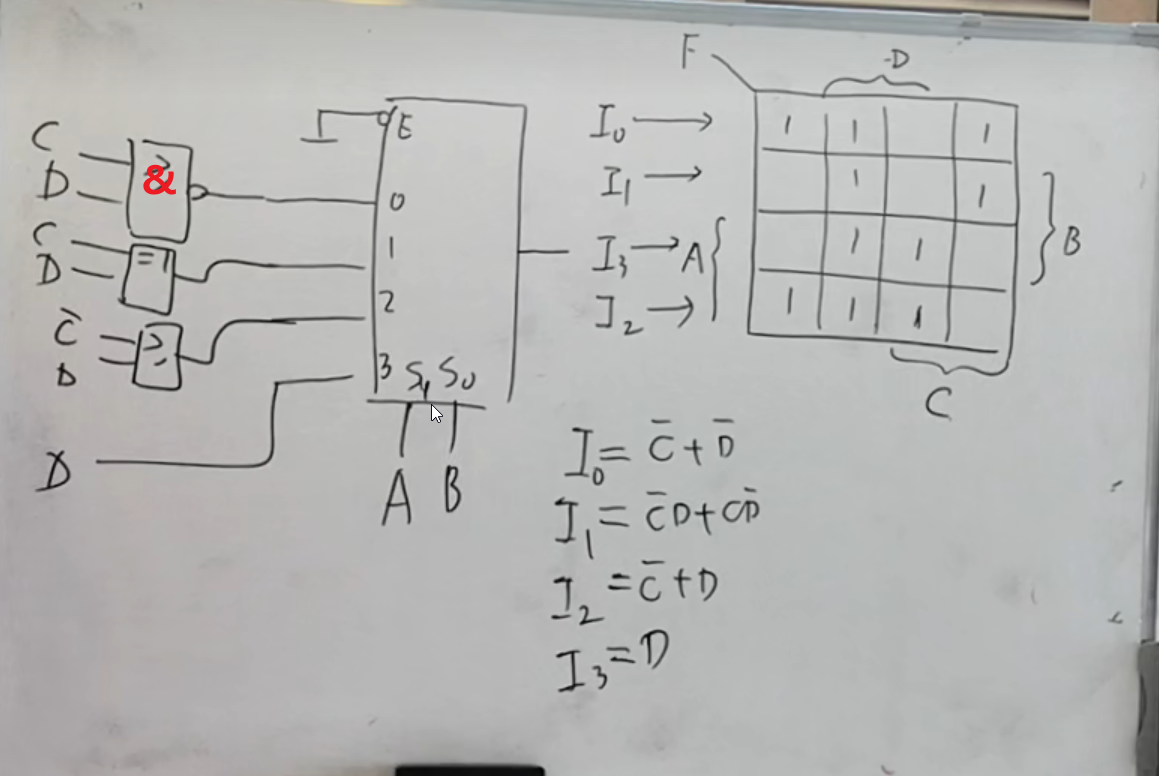
![[Java SE] 彻底搞懂Java程序的三大参数配置途径:系统变量与JVM参数(VM Option)/环境变量/启动程序参数args](https://img2023.cnblogs.com/blog/1173617/202306/1173617-20230609142845477-846259964.png)