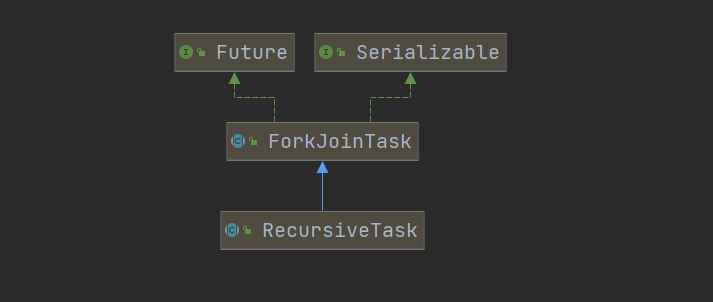
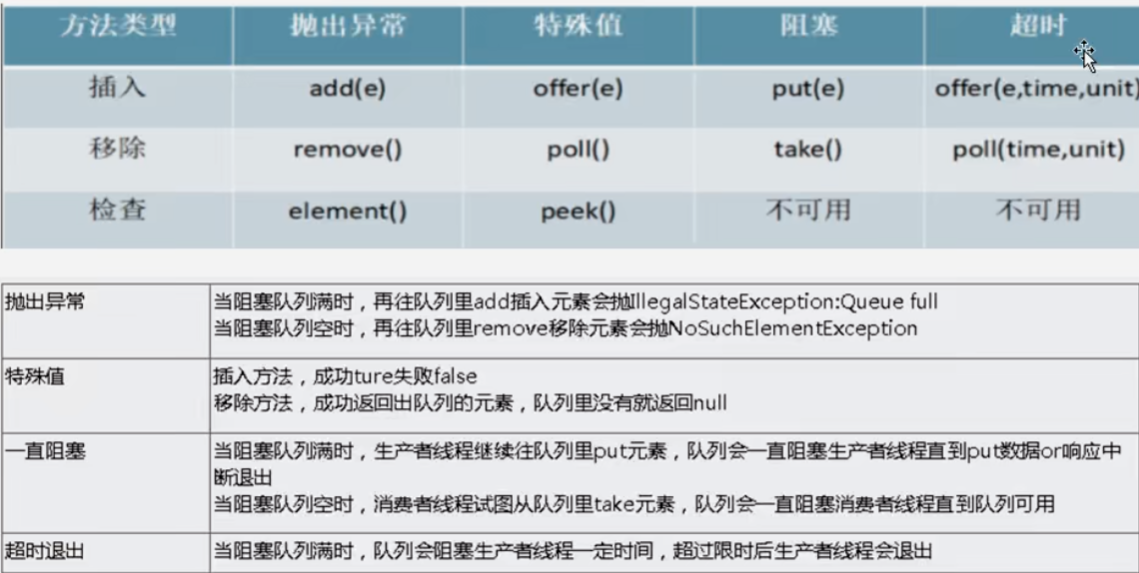
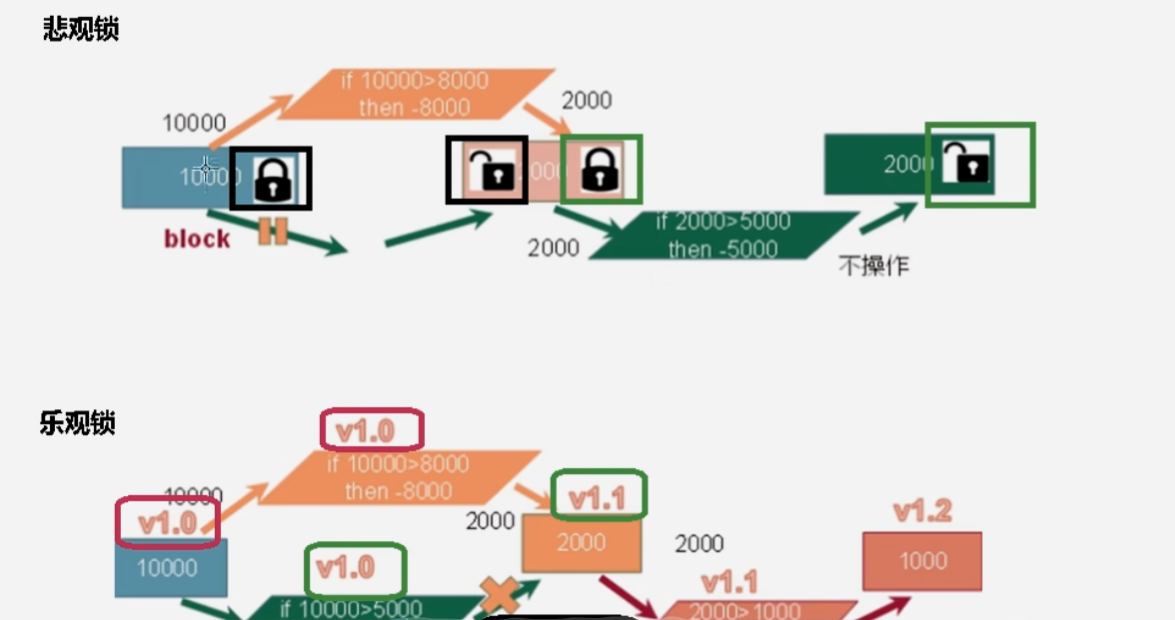
1 JUC简介
JUC就是java.util.concurrent的简称,这是一个处理线程的工具包,JDK1.5开始出现的。
进程和线程、管程
进程:系统资源分配的基本单位;它是程序的一次动态执行过程。系统运行一个程序即是一个进程从创建,运行到消亡的过程。
线程:系统资源调度的基本单位;它是一个比进程更小的执行单位。一个进程在执行过程中可以产生多个线程。同类的多个线程共享进程的堆和方法区资源,但是每个线程有自己的程序计数器、虚拟机栈和本地方法栈,所以系统在产生一个线程,或是在各个线程之间作切换工作时,负担要比进程小得多,也正因为如此,线程也被称为轻量级进程。
协程:一种比线程更加轻量级的存在。协程完全由程序所控制(在用户态执行),带来的好处是性能大幅度的提升。一个操作系统中可以有多个进程;一个进程可以有多个线程;同理,一个线程可以有多个协程。由于协程切换是在线程内完成的,所以涉及到的资源比较少,几乎只是切换了寄存器和协程栈的内容。
管程:共享资源访问模型
管程在操作系统中被称为Monitor对象,也就是Java中的锁
管程是一种同步机制,用于管理共享资源的访问过程,保证某个时刻只允许一个线程访问资源。
jvm同步就是基于进入退出临界区的时候使用管程对象来实现的,管程对象随着对象的创建而创建,随着对象的消亡而消亡
线程的状态
- NEW:创建
- RUNNABLE:运行
- BLOCKED:阻塞
- WAITING:等待
- TIMED_WAITING:等待(超时不再等待)
- TERMINATED:终结
public enum State {
/**
* Thread state for a thread which has not yet started.
*/
NEW,
/**
* Thread state for a runnable thread. A thread in the runnable
* state is executing in the Java virtual machine but it may
* be waiting for other resources from the operating system
* such as processor.
*/
RUNNABLE,
/**
* Thread state for a thread blocked waiting for a monitor lock.
* A thread in the blocked state is waiting for a monitor lock
* to enter a synchronized block/method or
* reenter a synchronized block/method after calling
* {@link Object#wait() Object.wait}.
*/
BLOCKED,
/**
* Thread state for a waiting thread.
* A thread is in the waiting state due to calling one of the
* following methods:
* <ul>
* <li>{@link Object#wait() Object.wait} with no timeout</li>
* <li>{@link #join() Thread.join} with no timeout</li>
* <li>{@link LockSupport#park() LockSupport.park}</li>
* </ul>
*
* <p>A thread in the waiting state is waiting for another thread to
* perform a particular action.
*
* For example, a thread that has called {@code Object.wait()}
* on an object is waiting for another thread to call
* {@code Object.notify()} or {@code Object.notifyAll()} on
* that object. A thread that has called {@code Thread.join()}
* is waiting for a specified thread to terminate.
*/
WAITING,
/**
* Thread state for a waiting thread with a specified waiting time.
* A thread is in the timed waiting state due to calling one of
* the following methods with a specified positive waiting time:
* <ul>
* <li>{@link #sleep Thread.sleep}</li>
* <li>{@link Object#wait(long) Object.wait} with timeout</li>
* <li>{@link #join(long) Thread.join} with timeout</li>
* <li>{@link LockSupport#parkNanos LockSupport.parkNanos}</li>
* <li>{@link LockSupport#parkUntil LockSupport.parkUntil}</li>
* </ul>
*/
TIMED_WAITING,
/**
* Thread state for a terminated thread.
* The thread has completed execution.
*/
TERMINATED;
}
wait & sleep
- wait:释放掉当前线程持有的锁,使当前线程进入一个等待队列处于等待状态(WAITING),直到其他线程调用此对象的notify()或notifyAll()方法唤醒线程。wait(long timeout)则是在指定时间内被其他线程唤醒,超过时间自动被唤醒。
- 强制当前正在执行的线程休眠(暂停执行),在苏醒之前不会返回到可运行状态,当睡眠时间到期,则返回到可运行状态。
区别
- sleep是Thread的静态方法,而wait是Object中的方法,任何对象实例都能够调用。
- sleep不需要占用锁也不会释放锁,而wait会释放锁,所以调用的前提是当前线程占有锁(即代码处于synchronized代码块中)。
- 它们都会被interrupted方法中断。
并发与并行
- 并发:所有任务按照一定的顺序执行,只有前面的任务执行完成后面的任务才能执行
- 并行:同时可以运行多个任务,单核处理器实际上是宏观上并行微观上串行。
用户线程和守护线程
- 用户线程:一般自定义的线程都属于自定义线程
- 守护线程:运行在后台的线程,如:垃圾回收线程,如果只剩下守护线程,则主线程结束守护线程也会结束
public static void main(String[] args) {
var thread = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "::" + Thread.currentThread().isDaemon());
while(true) {
}
});
thread.start();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " over");
}
main over
Thread-0::false且用户线程一直在运行,JVM不会结束
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
var thread = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "::" + Thread.currentThread().isDaemon());
while(true) {
}
});
thread.setDaemon(true);
thread.start();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " over");
}
}
main over
主线程结束,守护线程也结束(还没来得及运行),JVM也结束了
2 Synchronized
Synchronized是一种同步的可重入锁,可以修饰的对象有下面几种:
-
代码块,被修饰的代码块称作同步代码块
-
方法,被修饰的方法称作是同步方法,作用范围是整个方法,作用的对象是调用这个方法的对象
Synchronized不属于方法定义的一部分,因此不能被继承,子类不声明的话默认不是同步的
-
静态方法,作用范围是整个静态方法,作用对象是这个类的所有实例对象
-
一个类,作用范围是整个括号的部分,作用对象是这个类的所有实例对象
举例:售票员买票
分析:
资源类:票,属性:30张,操作方法:卖
public class TicketSale {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ticket ticket = new Ticket(3000);
Runnable r = () -> {
while(ticket.getNum() > 0) {
ticket.sale();
}
};
new Thread(r, "A").start();
new Thread(r, "B").start();
new Thread(r, "C").start();
}
}
class Ticket {
private int num;
public Ticket(int num) {
this.num = num;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.valueOf(this.num);
}
public synchronized void sale() {
if(this.num > 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +
" sale 1 ticket, there are " + --num + " tickets left" );
}
}
public int getNum() {
return this.num;
}
}
3 Lock接口
package java.util.concurrent.locks:为锁和等待条件提供的一个框架的接口和类,不同于内置同步和监视器。
可重入锁:可以重复使用的锁,即某个线程已经获得了某个锁,再次获取锁而不会出现死锁,可重入锁有:
- synchronized
- ReentrantLock:ReentrantLock 和 synchronized 不一样,需要手动释放锁,所以使用 ReentrantLock的时候一定要手动释放锁,并且加锁次数和释放次数要一样
class LTicket {
private int num = 30;
private final ReentrantLock lock;
LTicket() {
lock = new ReentrantLock();
}
public void sale() {
lock.lock();
try {
if(this.num > 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() +
" sale 1 ticket, there are " + --num + " tickets left" );
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
public class TicketSale {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LTicket ticket = new LTicket();
Runnable r = () -> {
for(int i = 0; i < 40; i++) {
ticket.sale();
}
};
new Thread(r, "A").start();
new Thread(r, "B").start();
new Thread(r, "C").start();
}
}
4 lock和synchronized的区别
- Lock是一个接口,synchronized是java语言关键字,是内置语言实现
- synchronized中发生异常,会自动释放占有的锁,而lock接口实现类需要手动释放,否则可能会导致死锁
- lock可以让等待的线程响应中断,而synchronized不会,等待的线程会一直等待下去
- 通过lock可以知道有没有获取成功锁,synchronized不行
- lock可以提高多个线程读的效率
- 资源竞争激烈的时候,lock的性能远远优于synchronized