1 前言
IMS启动流程 中介绍了 IMS 在 Java 层和 Native 层的初始化流程,以及创建 NativeInputManager、InputManager、InputReader、InputDispatcher、EventHub 等对象过程;View添加过程 中介绍了从 WindowManagerImpl 的 addView() 方法到 WindowState、SurfaceSession 的创建流程;本文将介绍 InputChannel 在 Java 层和 Native 层的初始化流程。
InputChannel 本质是对 Socket 的封装,用于输入事件跨进程通讯。
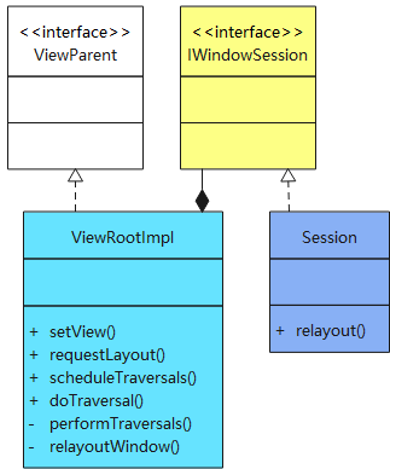
如图,浅蓝色的类是应用进程中执行的,深蓝色的类是在 system_server 进程中执行的;浅蓝色和深蓝色的都是 Java 层代码,绿色的是 JNI 层代码,紫色的是 Native 层代码。
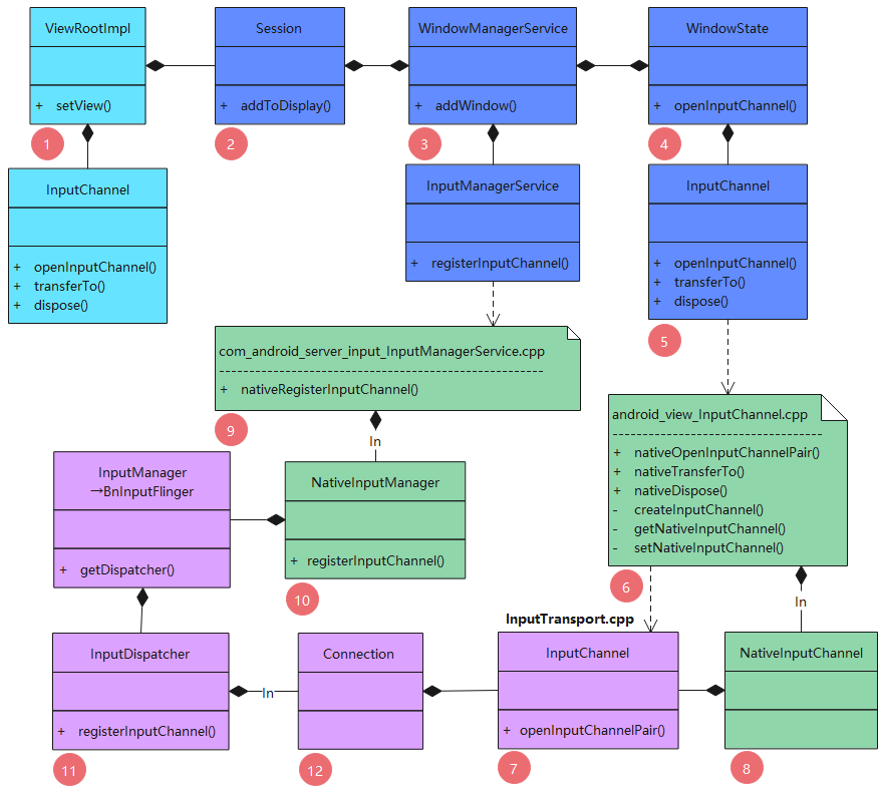
2 Java 层 InputChannel 初始化流程
(1)addView
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView) {
synchronized (this) {
if (mView == null) {
mView = view;
...
if ((mWindowAttributes.inputFeatures & WindowManager.LayoutParams.INPUT_FEATURE_NO_INPUT_CHANNEL) == 0) {
//创建 InputChannel,构造方法中什么也没干
mInputChannel = new InputChannel();
}
...
//请求显示 View
requestLayout();
if ((mWindowAttributes.inputFeatures & WindowManager.LayoutParams.INPUT_FEATURE_NO_INPUT_CHANNEL) == 0) {
mInputChannel = new InputChannel();
}
...
try {
...
res = mWindowSession.addToDisplay(mWindow, mSeq, mWindowAttributes, getHostVisibility(),
mDisplay.getDisplayId(), mTmpFrame, mAttachInfo.mContentInsets, mAttachInfo.mStableInsets,
mAttachInfo.mOutsets, mAttachInfo.mDisplayCutout, mInputChannel, mTempInsets);
setFrame(mTmpFrame);
}
...
if (mInputChannel != null) {
if (mInputQueueCallback != null) {
mInputQueue = new InputQueue();
mInputQueueCallback.onInputQueueCreated(mInputQueue);
}
//创建 WindowInputEventReceiver
mInputEventReceiver = new WindowInputEventReceiver(mInputChannel, Looper.myLooper());
}
}
}
}
说明:在 setView 过程中,创建了 InputChannel,说明每个窗口对应一个 InputChannel,这里创建了一个空的 InputChannel,mWindowSession.addToDisplay() 将创建的 InputChannel 对象传给system_server 进程,并在 WindowState 中实现初始化。
(2)addToDisplay
/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/Session.java
public int addToDisplay(IWindow window, int seq, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, int viewVisibility,
int displayId, Rect outFrame, Rect outContentInsets, Rect outStableInsets, Rect outOutsets,
DisplayCutout.ParcelableWrapper outDisplayCutout, InputChannel outInputChannel, InsetsState outInsetsState) {
//mService 为 WMS
return mService.addWindow(this, window, seq, attrs, viewVisibility, displayId, outFrame, outContentInsets,
outStableInsets, outOutsets, outDisplayCutout, outInputChannel, outInsetsState);
}
(3)addWindow
/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowManagerService.java
public int addWindow(Session session, IWindow client, int seq, LayoutParams attrs, int viewVisibility,
int displayId, Rect outFrame, Rect outContentInsets, Rect outStableInsets, Rect outOutsets,
DisplayCutout.ParcelableWrapper, InputChannel outInputChannel, InsetsState outInsetsState) {
...
synchronized (mGlobalLock) {
...
//创建 WindowState,说明每个根 View,都与一个 WindowState 一一对应
final WindowState win = new WindowState(this, session, client, token, parentWindow, appOp[0],
seq, attrs, viewVisibility, session.mUid, session.mCanAddInternalSystemWindow);
...
if (openInputChannels) {
//打开 InputChannel
win.openInputChannel(outInputChannel);
}
...
win.attach(); //mSessions.add(win.mSession)
mWindowMap.put(client.asBinder(), win);
...
win.mToken.addWindow(win); //win.mToken.addChild(win, mWindowComparator)
...
}
...
return res;
}
(4)openInputChannel
/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowState.java
void openInputChannel(InputChannel outInputChannel) {
...
String name = getName();
//创建 socketpair,nativeOpenInputChannelPair(name)
InputChannel[] inputChannels = InputChannel.openInputChannelPair(name);
mInputChannel = inputChannels[0]; //本地存留
mClientChannel = inputChannels[1]; //返给应用进程
mInputWindowHandle.token = mClient.asBinder();
if (outInputChannel != null) {
//nativeTransferTo(outInputChannel),将 outInputChannel 与 NativeInputChannel 绑定,mClientChannel 与 NativeInputChannel 解绑
mClientChannel.transferTo(outInputChannel);
//nativeDispose(false),将 mClientChannel 与 NativeInputChannel 解绑,并清除对应 NativeInputChannel
mClientChannel.dispose();
mClientChannel = null;
}
...
//inputChannel.setToken(token);
//nativeRegisterInputChannel(mPtr, inputChannel, Display.INVALID_DISPLAY),将 inputChannel 注入到 InputDispatcher 中
mWmService.mInputManager.registerInputChannel(mInputChannel, mClient.asBinder());
}
openInputChannel() 方法中调用了如下 4 个JNI 层的方法:
- nativeOpenInputChannelPair:创建 socket 客户端和服务端,并使用 InputChannel(Native 层) 封装;
- nativeTransferTo:将 outInputChannel 与 NativeInputChannel 绑定,mClientChannel 与 NativeInputChannel 解绑;
- nativeDispose:将 mClientChannel 与 NativeInputChannel 解绑,并清除对应 NativeInputChannel;
- nativeRegisterInputChannel:将 inputChannel 注入到 InputDispatcher 中,并创建 Connection 对象。
3 Native 层 InputChannel 初始化流程
本节主要介绍 WindowState 中调用的 InputChannel 和 IMS 中的 Native 方法,依次为:nativeOpenInputChannelPair、nativeTransferTo、nativeDispose、nativeRegisterInputChannel。
3.1 nativeOpenInputChannelPair 后续流程
InputChannel 的 openInputChannelPair() 方法调用了 JNI 层的 nativeOpenInputChannelPair() 方法,调用点如下。
//创建 socket 客户端和服务端,并使用 InputChannel(Native 层) 封装
InputChannel[] inputChannels = InputChannel.openInputChannelPair(name);
(1)gInputChannelMethods
/frameworks/base/core/jni/android_view_InputChannel.cpp
static const JNINativeMethod gInputChannelMethods[] = {
//Java 层调用的 nativeOpenInputChannelPair 方法对应 JNI 层的 android_view_InputChannel_nativeOpenInputChannelPair 方法
{ "nativeOpenInputChannelPair", "(Ljava/lang/String;)[Landroid/view/InputChannel;",
(void*)android_view_InputChannel_nativeOpenInputChannelPair },
//Java 层调用的 nativeDispose 方法对应 JNI 层的 android_view_InputChannel_nativeDispose 方法
{ "nativeDispose", "(Z)V",
(void*)android_view_InputChannel_nativeDispose },
//Java 层调用的 nativeTransferTo 方法对应 JNI 层的 android_view_InputChannel_nativeTransferTo 方法
{ "nativeTransferTo", "(Landroid/view/InputChannel;)V",
(void*)android_view_InputChannel_nativeTransferTo },
...
};
(2)android_view_InputChannel_nativeOpenInputChannelPair
/frameworks/base/core/jni/android_view_InputChannel.cpp
#include <input/InputTransport.h>
static jobjectArray android_view_InputChannel_nativeOpenInputChannelPair(JNIEnv* env, jclass clazz, jstring nameObj) {
...
sp<InputChannel> serverChannel; //服务端 InputChannel
sp<InputChannel> clientChannel; //客户端 InputChannel
//创建 socketpair,并创建 Native 层的 InputChannel
status_t result = InputChannel::openInputChannelPair(name, serverChannel, clientChannel);
...
jobjectArray channelPair = env->NewObjectArray(2, gInputChannelClassInfo.clazz, NULL);
...
jobject serverChannelObj = android_view_InputChannel_createInputChannel(env, std::make_unique<NativeInputChannel>(serverChannel));
...
jobject clientChannelObj = android_view_InputChannel_createInputChannel(env, std::make_unique<NativeInputChannel>(clientChannel));
...
//将 serverChannelObj、clientChannelObj 放入 channelPair
env->SetObjectArrayElement(channelPair, 0, serverChannelObj);
env->SetObjectArrayElement(channelPair, 1, clientChannelObj);
return channelPair;
}
说明:
- inputTransport.h 中定义了抽象的 InputChannel 类,inputTransport.cpp 实现 inputTransport.h 中的抽象方法;
- openInputChannelPair() 方法创建了socketpair,并创建了 Native 层的 InputChannel 对象,用于封装 socket;
- std::make_unique
(params)) 用于创建 T 类型对象,这里创建了 2 个 NativeInputChannel 对象,并将前面创建的 InputChannel(Native 层)对象注入; - android_view_InputChannel_createInputChannel() 方法将 JNI 层的 NativeInputChannel 对象封装为 Java 层的 InputChannel 对象;
- 一个 Java 层的 InputChannel 对象,对应一个 JNI 层的 NativeInputChannel 对象,对应一个 Native 层的 InputChannel 对象。
//new NativeInputChannel(serverChannel)
std::make_unique<NativeInputChannel>(serverChannel)
//new NativeInputChannel(clientChannel)
std::make_unique<NativeInputChannel>(clientChannel)
(3)openInputChannelPair
/frameworks/native/libs/input/InputTransport.cpp
status_t InputChannel::openInputChannelPair(const std::string& name, sp<InputChannel>& outServerChannel, sp<InputChannel>& outClientChannel) {
int sockets[2];
if (socketpair(AF_UNIX, SOCK_SEQPACKET, 0, sockets)) {
...
}
int bufferSize = SOCKET_BUFFER_SIZE;
setsockopt(sockets[0], SOL_SOCKET, SO_SNDBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof(bufferSize));
setsockopt(sockets[0], SOL_SOCKET, SO_RCVBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof(bufferSize));
setsockopt(sockets[1], SOL_SOCKET, SO_SNDBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof(bufferSize));
setsockopt(sockets[1], SOL_SOCKET, SO_RCVBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof(bufferSize));
//serverChannelName = name + " (server)"
outServerChannel = new InputChannel(serverChannelName, sockets[0]);
//clientChannelName = name + " (client)"
outClientChannel = new InputChannel(clientChannelName, sockets[1]);
return OK;
}
(4)InputChannel
/frameworks/native/libs/input/InputTransport.cpp
InputChannel::InputChannel(const std::string& name, int fd) :
mName(name) {
...
setFd(fd);
}
void InputChannel::setFd(int fd) {
...
mFd = fd;
if (mFd > 0) {
int result = fcntl(mFd, F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK);
...
}
}
fcntl() 为 Linux 层函数,其作用是:根据文件描述词来操作文件的特性(Linux fcntl函数详解);InputChannel 的构造方法中传入的 fd 参数为 openInputChannelPair() 方法中创建的 socket,由此可知,InputChannel 的本质是对 socket 的封装。
(5)NativeInputChannel
/frameworks/base/core/jni/android_view_InputChannel.cpp
NativeInputChannel::NativeInputChannel(const sp<InputChannel>& inputChannel) :
mInputChannel(inputChannel), mDisposeCallback(NULL) {
}
说明:inputChannel(Native层)是 openInputChannelPair() 方法中创建的 serverChannel 和 clientChannel。
(6)android_view_InputChannel_createInputChannel
/frameworks/base/core/jni/android_view_InputChannel.cpp
static jobject android_view_InputChannel_createInputChannel(JNIEnv* env, std::unique_ptr<NativeInputChannel> nativeInputChannel) {
jobject inputChannelObj = env->NewObject(gInputChannelClassInfo.clazz, gInputChannelClassInfo.ctor);
if (inputChannelObj) {
android_view_InputChannel_setNativeInputChannel(env, inputChannelObj, nativeInputChannel.release());
}
return inputChannelObj;
}
static void android_view_InputChannel_setNativeInputChannel(JNIEnv* env, jobject inputChannelObj, NativeInputChannel* nativeInputChannel) {
env->SetLongField(inputChannelObj, gInputChannelClassInfo.mPtr, reinterpret_cast<jlong>(nativeInputChannel));
}
android_view_InputChannel_createInputChannel() 方法将 JNI 层的 NativeInputChannel 对象封装为 Java 层的 InputChannel 对象。
3.2 nativeTransferTo 后续流程
InputChannel 的 transferTo() 方法调用了 JNI 层的 nativeTransferTo() 方法,调用点如下。
//将 outInputChannel 与 NativeInputChannel 绑定,mClientChannel 与 NativeInputChannel 解绑
mClientChannel.transferTo(outInputChannel);
(1)android_view_InputChannel_nativeTransferTo
Java 层调用的 nativeTransferTo() 方法对应 JNI 层的 android_view_InputChannel_nativeTransferTo() 方法。
/frameworks/base/core/jni/android_view_InputChannel.cpp
static void android_view_InputChannel_nativeTransferTo(JNIEnv* env, jobject obj, jobject otherObj) {
...
//获取与 obj 绑定的 NativeInputChannel 对象
NativeInputChannel* nativeInputChannel = android_view_InputChannel_getNativeInputChannel(env, obj);
//将 otherObj 与 nativeInputChannel 绑定
android_view_InputChannel_setNativeInputChannel(env, otherObj, nativeInputChannel);
//将 Obj 与 nativeInputChannel 解绑
android_view_InputChannel_setNativeInputChannel(env, obj, NULL);
}
说明:obj 指 Java 层的 mClientChannel;otherObj 指 Java 层 的 outInputChannel。
(2)android_view_InputChannel_getNativeInputChannel
/frameworks/base/core/jni/android_view_InputChannel.cpp
static struct {
jclass clazz;
jfieldID mPtr; // native object attached to the DVM InputChannel
jmethodID ctor;
} gInputChannelClassInfo;
static NativeInputChannel* android_view_InputChannel_getNativeInputChannel(JNIEnv* env, jobject inputChannelObj) {
jlong longPtr = env->GetLongField(inputChannelObj, gInputChannelClassInfo.mPtr);
return reinterpret_cast<NativeInputChannel*>(longPtr);
}
说明:inputChannelObj 指 Java 层的 mClientChannel,每个 Java 层的 InputChannel 对应一个 JNI 层的 NativeInputChannel。
(3)android_view_InputChannel_setNativeInputChannel
/frameworks/base/core/jni/android_view_InputChannel.cpp
static void android_view_InputChannel_setNativeInputChannel(JNIEnv* env, jobject inputChannelObj, NativeInputChannel* nativeInputChannel) {
env->SetLongField(inputChannelObj, gInputChannelClassInfo.mPtr, reinterpret_cast<jlong>(nativeInputChannel));
}
说明:obj 指 Java 层的 mClientChannel 或 outInputChannel。
3.3 nativeDispose 后续流程
InputChannel 的 dispose() 方法调用了 JNI 层的 nativeDispose() 方法,调用点如下。
//nativeDispose(false),将 mClientChannel 与 NativeInputChannel 解绑,并清除对应 NativeInputChannel
mClientChannel.dispose();
(1)android_view_InputChannel_nativeDispose
Java 层调用的 nativeDispose() 方法对应 JNI 层的 android_view_InputChannel_nativeDispose() 方法。
/frameworks/base/core/jni/android_view_InputChannel.cpp
static void android_view_InputChannel_nativeDispose(JNIEnv* env, jobject obj, jboolean finalized) {
//获取与 obj 绑定的 NativeInputChannel 对象
NativeInputChannel* nativeInputChannel = android_view_InputChannel_getNativeInputChannel(env, obj);
if (nativeInputChannel) {
...
nativeInputChannel->invokeAndRemoveDisposeCallback(env, obj);
//将 obj 与 NativeInputChannel 解绑
android_view_InputChannel_setNativeInputChannel(env, obj, NULL);
//清除对应 NativeInputChannel
delete nativeInputChannel;
}
}
3.4 nativeRegisterInputChannel 后续流程
WindowState 的 openInputChannel() 方法调用了 IMS 的 registerInputChannel() 方法,调用点如下。
mWmService.mInputManager.registerInputChannel(mInputChannel, mClient.asBinder());
(1)registerInputChannel
/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/input/InputManagerService.java
public void registerInputChannel(InputChannel inputChannel, IBinder token) {
...
if (token == null) {
token = new Binder();
}
inputChannel.setToken(token);
//mPtr 为指向 NativeInputManager 的指针
nativeRegisterInputChannel(mPtr, inputChannel, Display.INVALID_DISPLAY);
}
(2)gInputManagerMethods
/frameworks/base/services/core/jni/com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp
static const JNINativeMethod gInputManagerMethods[] = {
...
//Java 层调用的 nativeRegisterInputChannel 方法对应 JNI 层的 nativeRegisterInputChannel 方法
{ "nativeRegisterInputChannel",
"(JLandroid/view/InputChannel;I)V",
(void*) nativeRegisterInputChannel },
...
}
(3)nativeRegisterInputChannel
/frameworks/base/services/core/jni/com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp
static void nativeRegisterInputChannel(JNIEnv* env, jclass, jlong ptr, jobject inputChannelObj, jint displayId) {
//获取 NativeInputManager
NativeInputManager* im = reinterpret_cast<NativeInputManager*>(ptr);
//获取与 inputChannelObj 绑定的 Native 层的 InputChannel 对象
sp<InputChannel> inputChannel = android_view_InputChannel_getInputChannel(env, inputChannelObj);
...
status_t status = im->registerInputChannel(env, inputChannel, displayId);
...
android_view_InputChannel_setDisposeCallback(env, inputChannelObj, handleInputChannelDisposed, im);
}
说明:ptr 为指向 NativeInputManager 的指针,NativeInputManager 在 IMS 初始化时创建,详见→IMS启动流程;inputChannelObj 为 Java 层的 InputChannel。
(4)android_view_InputChannel_getInputChannel
/frameworks/base/core/jni/android_view_InputChannel.cpp
sp<InputChannel> android_view_InputChannel_getInputChannel(JNIEnv* env, jobject inputChannelObj) {
//获取与 inputChannelObj 绑定的 NativeInputChannel 对象
NativeInputChannel* nativeInputChannel = android_view_InputChannel_getNativeInputChannel(env, inputChannelObj);
//转换为 InputChannel
return nativeInputChannel != NULL ? nativeInputChannel->getInputChannel() : NULL;
}
(5)registerInputChannel
/frameworks/base/services/core/jni/com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp
status_t NativeInputManager::registerInputChannel(JNIEnv* , const sp<InputChannel>& inputChannel, int32_t displayId) {
...
return mInputManager->getDispatcher()->registerInputChannel(inputChannel, displayId);
}
说明:NativeInputManager 为 JNI 层的类,InputManager 为 Native 层的类,它们在 IMS 初始化时就已创建,mInputManager 属于 InputManager 类;这里将 InputChannel 注册到 InputDispatcher 中。
(6)registerInputChannel
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/InputDispatcher.cpp
status_t InputDispatcher::registerInputChannel(const sp<InputChannel>& inputChannel, int32_t displayId) {
...
{ // acquire lock
...
//创建 connection
sp<Connection> connection = new Connection(inputChannel, false);
int fd = inputChannel->getFd();
mConnectionsByFd.add(fd, connection);
mInputChannelsByToken[inputChannel->getToken()] = inputChannel;
mLooper->addFd(fd, 0, ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT, handleReceiveCallback, this);
} // release lock
mLooper->wake(); //唤醒 Looper
return OK;
}
说明:Connection 是 InputDispatcher 的内部类。
(7)Connection
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/InputDispatcher.cpp
InputDispatcher::Connection::Connection(const sp<InputChannel>& inputChannel, bool monitor) :
status(STATUS_NORMAL), inputChannel(inputChannel),
monitor(monitor),
inputPublisher(inputChannel), inputPublisherBlocked(false) {
}
说明:在 Connection 的构造放方法中注入 inputChannel 和 monitor 属性。
声明:本文转自【framework】InputChannel创建流程